Unit 1
What is communication?
Communication is an Exchange of facts, ideas, opinions, or emotions by two or more persons.
Peter Little in his book Communication in Business defines communication as a process by which information is transmitted between Organization so that an understanding response is the result.
William Scott defines communication as a process that touches all aspects of human life, whether personal or professional.
Communication comes from the Latin word communis.
Types of communication.
1. On the basis of ways.
A. one way communication
Example. Ministers speech in meeting.
B. Two way communication.
Example. Shopkeeper and customer.
2. On the basis of content.
A. Verbal
Eg. Written and oral
B. Non verbal
Eg. Sign language used by ancient teibe
3. On the basis of decorum
A. Formal
Eg. Interview
B. Informal
Eg. Taking among friends
4. On the basis of pattern
A. Downward
Eg. Principle to Gardner
B. Upward
Eg. Gardener to principle
C. Diagonal
D. Horizontal ( same level )
E. Vertical
5. On the basis of address
A. Interpersonal
Eg. Talk between two friends
B. Intrapersonal
Eg. Talk within the person
6. Whole Communication
As a form of communication, whole communication refers to an interaction where the sentiments, emotions, interest, motives of all the participants, including the sender and the receiver, are taken into account.
Ideally speaking whole Communication is the best form of communication if it can be undertaken in practical terms. Here no response or no feedback from any communicator will go in vain.
Example. Family talk on the prospect of some family function.
7. Grapevine Communication ( group discussion)
Grapevine communication is an informal and unofficial way of communicating with an organization or social group. It involves the exchange of information, gossip, speculations and rumors among individuals using informal channels instead of official formal channels. It has no defined structure or agenda.
Process of Communication
Nature of Communication
Importance of Communication
Barriers of Communication
Unit 2
Business Letters
Why business letters?
1. Tool of future preference.
2. Convenience of documentation.
3. Ambassador of Goodwill.
4. Service as legal device.
5. multiplicity of business condition
Types of business letters.
1. Enquiry.
2. Quotation.
3. Order. Letter of execution.
4. Request.
5. Positive reply.
6. Negative reply.
7. Complained.
8. Adjustment.
9. Good news.
10. Bad news.
3 dimensions in business letter.
1. Mechanical.
2. Structural.
3. Stylistic.
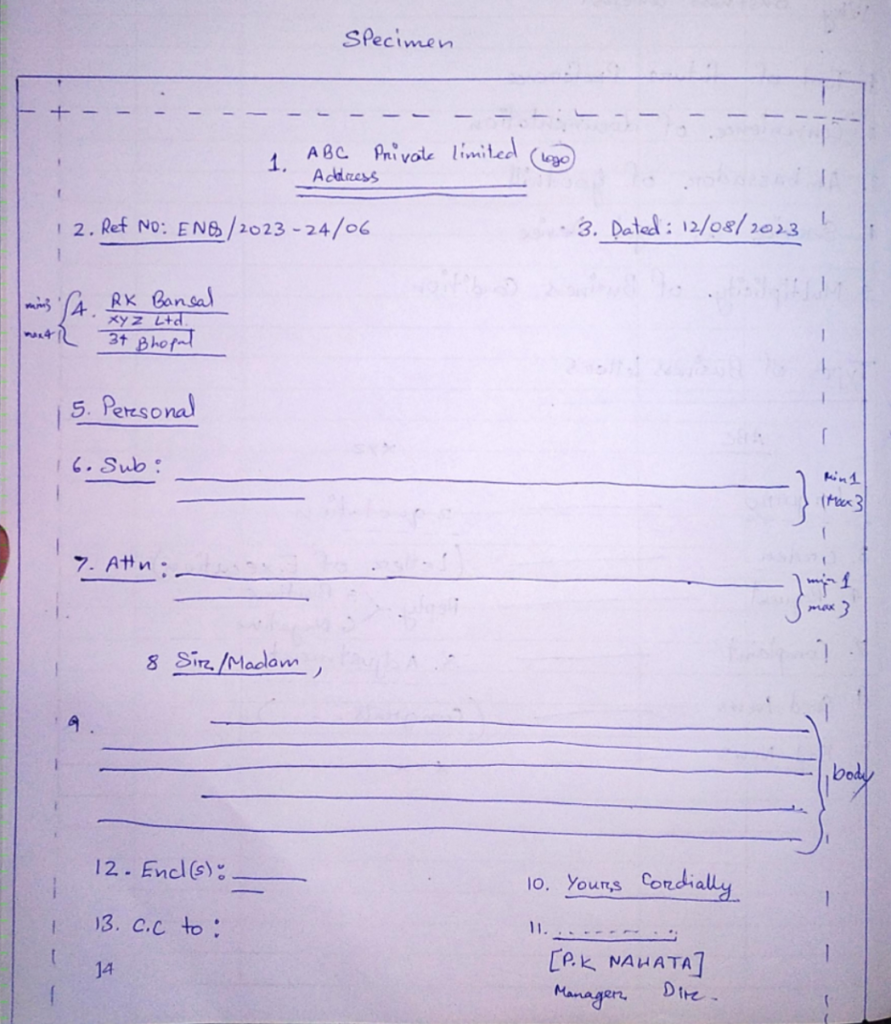
1. Mechanical Dimensions
1. Heading.
Heading consist of name of organization, address and logo.
2. Reference number. Inquiry number.
3. Date.
4. Inside address.
5. Personal or confidential note.
6. Subject.
7. Attention line. It is written during urgency, emergency or immediacy.
8. Salutation.
9. Body.
10. Complementary close.
11. Signature with name and designation.
12. And closer. List of attachment one sending along with the letter.
13. Carbon copy. Written for Official Coordination for National Organizational Issues.
14. Identification initials.
2. Structural Dimensions.
Format of writing letters.
Theoretically there are 7 formats, but practically 4 formats.
Formats.
1. Indented
It is the most popular, but it is outdated.
2. Full block.
It is used in late 1980s. Contemporary with Computer revolution? It is newer than indented. Convenient for short letters.
3. Modified block.
It is a combination of indented and full block.
Most updated.
Mostly contemporary.
4. Hanging indented.
Most elegant format than earlier.
Suitable for writing long letters.
Combination of modified block and indented.
3. Stylistic dimension.
Maintaining paragraphs in business letters.

Inquiry letter.
It is the first letter in business correspondence.
First paragraph.
1. Reference of the source of information.
2. Show some willingness.
Second paragraph.
1. Reputation of your organization.
2. Details of information short.
3. Possibility of ordering.
3rd paragraph.
1. Hope for reply.
2. Hope for continuing business relationship.
Question.
Imagine yourself as Mr/Mrs Anwar/Anwara Timur, the MD of Ujjal Electronics at Fancy Bazar Guwahati. Write an enquiry letter to Reliable Wholesale Electricals of station road, Bhopal asking about the price list and catalogue of some of their products.


Quotation Letter
First paragraph.
1. Thanks for inquiry.
2. Willingness to reply.
Second paragraph.
1. Details of information requested for.
2. Mode of payment, transportation, discount, etcetera.
3. Any specification in regard to the product.
3rd paragraph.
1. Hope For order.
2. Hope for continuing the relationship.
Question.
Suppose you are Mr. Samay Barma, the proprietary of excellent watches of BR Ambedkar Road of Bengaluru. Write the reply to the enquiry made by Rajendra Jajodya of SC Road of Alipuduar, West Bengal about the prices of various watches. (Full block format )



Order letter
First paragraph.
1. Reference to the quotation letter received.
2. Readiness to order.
Second paragraph.
1. Order in details. In tabular form in exam in separate sheet in real business.
2. Mode of payment, expected date of delivery, discount, guarantee, warranty, etcetera.
3. Reminder to the quality of product or service.
3rd paragraph.
1. Willingness to order next, if Positive.
2. Hope for continuing business relationship.
Question.
Pratinidi Enterprise of Babu Para Road, is in need of certain copying machines and other machineries from sterling machineries situated at Vivekananda Road , Azmair Rajasthan. Write an order letter on behalf of LM Xemka of Pratinidhi Enterprise in a situation of urgency. ( Modifying Block Format )



