Management information system.
Management Information System is the plant system of collecting, storing and disseminating data in the form of information needed to carry out the functions of management.
Components of MIS.
1.Management.
It covers the planning, control and administration of the operations of an organization. The top management handles planning, the middle management focuses on controlling, while the lower management is concerned with actual administration.
2. Information.
This means the process data that helps the management in planning, controlling and operations. Data means all the facts arising out of the operations of the organization. This data is processed, that is recorded, summarized, compared and finally presented to the management in the form of MIS reports.
3. System.
Data is processed into information with the help of a system. The system is made-up of inputs, processing, output, and feedback or control.
Objective of MIS.
1.Capturing data.
MIS captures contextual data or operational information that contribute in decision making from various internal and external sources of the organization.
2.Data processing.
The capture data is processed into information needed for planning, organizing, coordinating, directing and controlling functionalities, heads, strategic, tactical and operational levels.
Data processing involves.
A. Making calculations with that data.
B. Shorting data.
C. Classifying data.
D. Summarizing data.
3.Information Storage.
MIS stores stop process data or information for future use.
4.Information retrieval.
The stored information must be retrieved from the storage space as and when required by various users.
5. Information propagation.
Information of the MIS should be circulated to the users periodically using the organizational network.
Characteristics of MIS.
1.It should be based on long term planning.
2.It should provide a holistic view of the dynamics and the structure of the organization.
3.It should work as a complete and comprehensive system connecting all sub systems interconnected within the organization.
4.It should be planned and implemented in a top down order.
5.It should be based on the need of strategic, operational and tactical information of managers of an organization.
6.It should be able to make forecast and estimates and generate advance information for the benefit of decision makers within the organization.
7.It should provide real time information regarding ongoing events without any delay or time lag.
8.It should have a strong central database that fully supports information storage and retrieval.
9.It should allow easy flow of information, simplified and operation and avoid data redundancy and duplicity.
10.It should be built in a flexible manner so that it can be easily split into smaller subsystems as and when needed.
Functions of MIS.
The main function of MIS is to report on business operations. To support decision making and ensure efficient management of the organization. It aims to help the organization achieve its full potential and thereby gain competitive advantage over its competitors.
MIS has the following important functions.
1. Easy access to information.
MIS allows the management continued access information related to marketing, finances or operations.
MIS reports strategically stored large amount of information about the business in a central location that managers can easily access over a network.
2. Data collection.
And MIS collects daily data from the companies day-to-day operation and combines the same with data from outside sources.
This allows the healthy and functional relationship between distributors to the point of sales and any other Supply chain member.
3. Performance tracking.
MIS plays a crucial role in keeping track of employee performance that enables managers to quickly take management decisions using the latest information.
4. Workplace collaborations.
MIS is an effective communication channel for teams to collaborate and ensure that the decision making group can access all the data needed for effective decision making, even while working from a different location.
5. Future projection.
The trend analysis features available in an MIS allows the management to determine how a business will perform in the correct configuration and how it will be affected if certain changes are implemented.
Advantages of MIS
1. It allows company management to access a single database for managing all transactions and planning processes.
2. Saves time and increases work efficiency.
3. It assures improved data analysis and decision making.
4. It maintains an accurate record of the system inputs and outputs and tracks employee performance.
5. It can critically analyse the strength and weakness of an organization and its employees.
6. It allows the top level management to gain greater control over the organization’s finances and operations.
Disadvantages of MIS
1. It cannot solve all problems of an organization, and new challenges keep coming up for organizations over the period of time.
2. It involves high cost for maintenance and employee training requirements.
3. It is highly dependent on updated primary data and works good only if the company data is updated on a regular or periodic basis.
4. MIS will not serve the management and will become irrelevant if it is not designed keeping in mind the present and future needs of the organization.
Also, the MIS will be rendered useless if it is not open to technical upgradation or future enhancements.
5. Most information provided by the MIS is in quantitative form as it ignores qualitative information like employee behavior and so on.
Features of MIS.
1. Data integration.
An MIS integrates data from various departments and functions, giving decision makers A comprehensive view of the organization’s data.
2. Data storage.
MIS stores vast amounts of data in databases, making it accessible and retrievable whenever needed.
3. Data processing.
It processes data to generate meaningful information. It can also perform calculations, comparisons and other data transformations to produce reports and insights.
4. A real time information.
It offers real time data updates to ensure that decision makers can make timely decisions by accessing the latest information.
5. Report generation.
it generates various reports like standard reports, ad hoc reports and exception reports to help The management monitor employee performance and make informed decisions.
6. Security.
It restricts access to sensitive information and also prevents unauthorized access to the data.
7. Remote accessibility.
It can be accessed from any location, allowing decision makers to retrieve information remotely.
8. Mobile compatibility.
Most modern MIS are compatible with mobile devices, allowing users to access critical information on the move.
9. Data Analytics.
Some advanced MIS can incorporate data analytics and business intelligence tools to provide deeper insights and supportive predictive analytics.
10. Customization.
It can be customized to fulfill the needs of an organization and also modify the way information is presented.
Data processing.
It refers to processing of data, that is to convert its format.
Data processing converts the usually available data into something more informative and useful. A data processing process system Is also known as Information System.
The processing of data can be expressed as.
A. Process of conversion of data in a format understandable by the computer.
B. Sorting or processing of data by a computer.
Stages of data processing.
Data processing process involves a series of stages to transform raw data into meaningful information. The fundamental stages of data processing process are as follows.
1. Collection.
The process begins with the collection of raw data from various sources. This stage establishes the foundation for subsequent processing, ensuring A comprehensive pool of data relevant to the intended analysis. It includes Surveys. Sensors., databases, or any other means of gathering relevant information.
2. Preparation.
It refers to data organizing, data cleaning and formatting raw data. Irrelevant information is filtered out And data is structured in a way that facilitates efficient analysis during subsequent stages of processing.
3. Input.
During this stage, the prepared data is entered into a computer system. This can be achieved through manual entry or automated methods depending on the nature of data and systems in place.
4. Processing.
This stays involves manipulating and analyzing the prepared data by extracting meaningful insights and patterns using operators such as sorting, summarizing, calculating, aggregating, etc.
5. Output.
During this stage, the results of data processing are presented in a comprehensive format through report , charts, graphs or other visual representations that facilitate understanding and decision making based on the analyzed data.
6. Storage
This stage involves storing the process data for future reference and analysis.
This is crucial for maintaining A stoical record, enabling efficient retrieval and supporting ongoing or future date related initiative. Proper data stories ensures the longetivity and accessibility of valuable information.
Data Process management method.
There are three main data processing methods which are as follows.
1. Manual data processing.
It relies on human effort to manage and manipulate data. It involves tasks such as sorting, calculating and recording information without the use of machines or electronic devices. This method Is relevant in situation where human personal task is necessary.
2. Mechanical data processing.
This method involves the use of machines like punch cards or mechanical calculators to handle data. It offers increased efficiency over manual data processing method, but lacks the speed and sophistication of electronic systems.
3. Electronic data processing.
This method uses computers and these cell technology to perform data related task. It tells significantly enhance data, processing speed, accuracy and capacity.It includes various techniques like maths processing, real time processing, online processing, etcetera.
Data processing types.
1. Manual processing.
In this, type, data is processed by humans without the use of machines or electronic devices. It involves tasks such as manual calculation, shorting and reordering, making it a time consuming process.
2. Mechanical processing.
This method utilizes mechanical methods, such as ones called on mechanical calculation to process data. It is more efficient than manual processing.
3. Electronic processing.
It is also known as Electronic Data processing. It involves use of computers to process and analyze data. It has immense speed and accuracy as compared to manual and mechanical methods.
4. Batch processing.
It involves grouping data into batches and processing them together at a scheduled time. It is suitable for non time sensitive tasks and is efficient for large scale data processing.
5. Real time processing.
It deals with data immediately as it is generated. It is crucial for time sensitive application Like financial transaction.
6. Online processing.
Also known as online transaction processing. It involves processing data directly while it is being collected. It is interactive and supports concurrent transaction, making it suitable for applications that require simultaneous use.
7. Automated processing.
This method is known as Automatic Data Processing and refers to the use of computers and software to automate data processing task. It includes various methods like batch processing and real time process to effectively handle large values of data with minimum human intervention.
Architecture of Information System.
The architecture of an information system includes the hardware and software used to deliver the solution to the final consumer of services.
This architecture is a description of the design and contents of a computerized system. If documented, the architecture may include information such as a detailed inventory of current hardware, software, and networking capabilities. A description of long range plans and priorities for future forces, and they plan for upgrading or Replacing dated equipment and software.
The architecture should also document the following.
A. What data is stored?
B. How the system functions?
C. Where are the components located?
D. When do activities and events occurred in the system?
E. Why does the system exist?
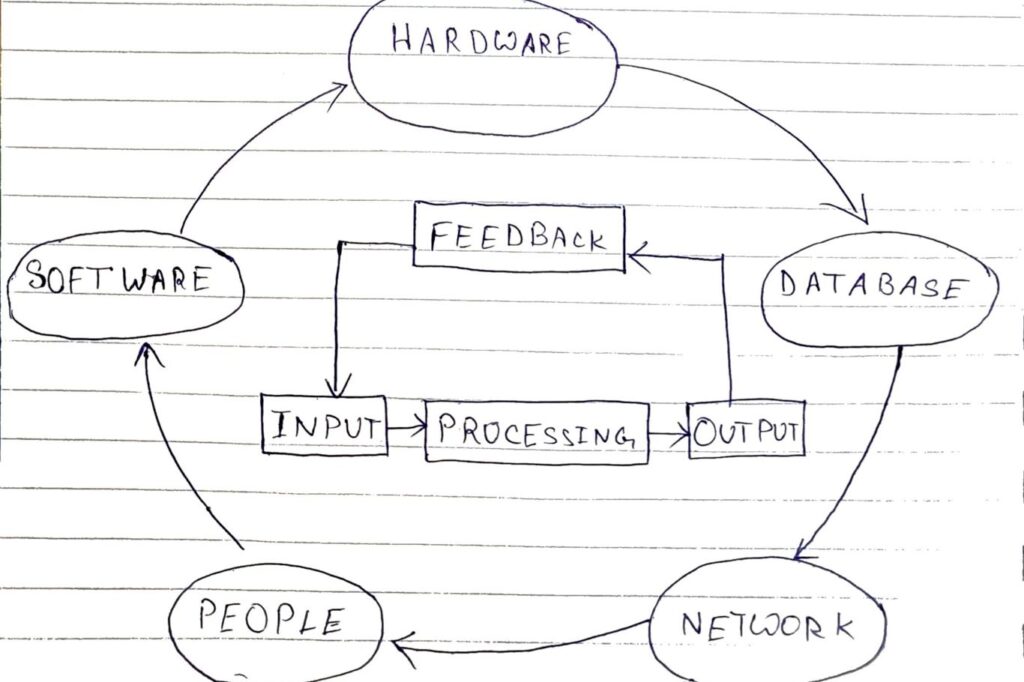
Figure. Information System Architecture and Components.
Components of information systems.
There are 5 main resources of information system which are as follows.
1. Hardware resources.
They refer to all physical devices that are used in the processing of information.
It not only includes computers and other equipments, but also any tangible object in which data can be stored.
Some hardware resources are.
A. Computer peripherals.
These devices are used in the computer to input data, store data and provide the output.
For example. For example. Keyboard is used for data input. Printer for output information. Magnetic tapes for storing information.
B. Computer systems.
These comprised of a central processing unit containing microprocessors and numerous interconnected peripheral devices.
Examples. Handheld devices, laptops, desktop computers, mainframe and micro computer systems.
2. People resources.
People play a crucial role for effective operation of all information systems.
The different type of people resources are as follows.
A. Information system specialist.
These are people who develop and operate information systems. It includes system analysts, software developer, system operators, managerial and technical personnel.
B. End users or clients
These are users who use the information produced by an information system. They include customers, sales people, engineers, accountants, clerks or managers.
Matrix University Donation :
Help us to create such notes for next year also by donating any amount you want .
Your donation will be used to buy internet servers, which costs around Rs 5,000 .
Thank you
Deepjal Mandal
[Founder: Matrix University]
