Unit 1
Key elements of organizational behavior.
1. The people.
People are at the core of organizational behavior.
They form the workforce of the organization and their interactions, behaviors, and attitudes significantly impact the organization’s functioning.
Understanding how people behave individually and in groups is crucial for effective management.
2. Structure.
Organizations are social systems.
There are two types of social system that exist side by side in an organization.
One is the formal and other informal social system.
The formal relationship of people in organization is called structure.
Different jobs are required to accomplish the organizational goals and objectives.
For example, there are managers and employees, accountants and assemblers.
These old people performing different jobs as different level have to be related in some structural way so that their work can be effectively coordinated.
People need organization, and organization need people come under the purview of organizational behavior.
It means that organizational behavior is based on visuality of interest.
3. Technology.
The technology provides the resources with which the people work and also effects the tasks they perform.
The main benefit of technology is that it allows people to do more and better work.
But it also restricts people from doing things in various ways.
4. Environment.
All organization operate within a given internal and external environment. In fact, no organization exist upon.
An organization is a part of larger system that combines other factors and elements such as the government, family and other organization.
All these mutually influence one another in a complex way.
Nature of organizational behavior.
Organizational behavior has a separate field of study. It’s nature and characteristics are similar.
1. A Separate field of study and not the discipline one.
By definition, a discipline is an accepted science that is based on a theoretical condition, but organizational behavior has a multi-interdisciplinary orientation and hence does not based on a specific theoretical background.
Therefore, it is better reasonable to call organizational behavior as a separate field of organizational behavior rather than a disciplines organizational behavior.
2. An interdisciplinary approach.
Organizational behavior is essential and Interdisciplinary approach to study human behavior and work.
It tries to implement the knowledge drawn from related disciplines like psychology, sociology and anthropology to make that applicable for studying and analyzing organizational behavior.
3. An applied science.
The very nature of organizational behavior is applied.
What organizational behavior basically does is the application of various resources to solve the organizational problems related to human behavior.
The basic line of different between pure science and organizational behavior is that while the former concentrates on fundamental resources, the latter applied resources.
Due to this purpose, organizational behavior can be called both sides as well as art.
4. Normative Science.
Organizational behavior is a normative science also because organizational behavior prescribes how the finance of applied resources can be applied to socially accepted organizational goals.
Thus, organizational behavior deals with what is accepted by individuals and society engaged in an organization.
5. A humanistic and optimistic approach.
Organizational behavior applies humanistic approach towards people working in the organization. It treats people as thinking and feeling human beings.
Organizational behavior is based on the belief that people have an innate desire to be independent, creative, and productive.
It also realizes that people working in the organization can and will actualize its potential if they are in proper condition and environment.
6. Total system approach.
The system approach is developed by the behavioral scientist to analyze human behavior in view of his or her social psychological framework.
Human beings social psychological framework is a complex 1 and the system approaches, tries to study his or her complexity and tries to find a solution to the same.
Scope of organizational behavior.
Organizational behavior is the study of human behavior at work in organization.
Accordingly, the scope of organizational behavior includes the study of individuals, groups, and organizational structure.
1. Individuals.
The organization run by individuals. Individuals differ in many respects.
The study of individual therefore includes such as personality, perception, attitudes, values, job satisfaction, learning and modulation.
2. Groups of individuals.
It includes aspects such as group dynamics, group conflicts, communication, leadership, power and politics.
3. Organization or structure.
The study of organization or structure includes aspects such as formation of organization, structure, culture change, and development.
In a nutshell, organizational behavior studies how organization influence people or how people influence organization.
Contributing disciplines to OB
Organizational behavior is an applied behavioral science.
It has grown from a number of under applied interdisciplinary sociology, anthropology, political science, science, technology, etc.
A brief description is given below.
1. Psychology.
The discipline that has had the greatest influence on the field of organizational behavior is psychology.
It is a science that focuses directly on understanding and predicting individual behavior.
It has greatly contributed to the interpersonal dynamics of human behavior.
2. Sociology.
Sociology is the study of people in relation to their fellow human beings.
Whereas the psychologist focuses on the individual, sociologists study groups of individuals.
The field of sociology had contributions to our understandings of group dynamics within organizations.
3. Anthropology.
It is the study of societies to learn about human beings and their attitudes.
It helps us understand differences in fundamental values, attitudes, and behavior between people in different regions and organization.
Organization Create a unique culture that influence the way organizational members think about the organization and how they should behave.
4. Engineering.
It also influenced the study of organizational behavior.
Some topics are common to engineering as well as organizational behavior.
For example, work measurement, productivity measurement, work design, job design, workflow analysis.
5. Economics.
It study the production, distribution and consumption of goods and services.
Students of organizational behavior shared economic interest in such areas as labor market dynamics, productivity, human resource planning, and cost benefit analysis.
6. Political Science.
In recent time, political science also started seeking the attention of the organizational behavior.
Political science is usually thought of as the study of political systems.
But scientists are interested in how and why people acquire power, political behavior, decision making, conflict, the behavior of interest groups, and collision formation.
These are lateral areas of interest in organizational behavior.
In an organization, people strive for power and leadership recognition.
Political science helps in management In an effective and efficient manner.
7. Science.
It is a systematized body of knowledge.
The scientific methods attempts to produce information that is objective in the sense that it is certifiable and independent of a person’s opinions or preferences.
Scientific methods is the backbone of organizational behavior.
Organizational behavior is based on the systematic study of facts, behavior, deterioration, ships, and predictions.
The cause and effect relationship is also established the organizational behavior like that of science.
The verification of relationship and its quantification has added to the importance of organizational behavior.
8. Technology.
The level of technological development affects the view of the Employees.
Modern age is the age of computerization and Digitalization.
It has come within the framework of the model of organizational behavior.
The study of technological development is becoming essential for understanding the organizational behavior because people are influenced by the technological development.
Technology changes consumer behavior, distribution and storage activities.
9. Medicine.
It has also come in connection with the human behavior at work.
Stress is becoming a very common problem in organization as well as in the people working in the organization.
Research shows that controlling the causes in and out of organizational setting is important for the well-being of the organization.
Study of organizational behavior is important.
Organizational behavior is the study of people at work in organization.
We study because this plan interacting with them.
If all the work stays in the field.
We play our roles or parts on an organization stage.
That study of organizer behavior is important due to the following reasons.
1. It helps us understand ourselves and others in a better way. This helps greatly improving our interpersonal relations in the organization. Friendly and cordial relations between employees and management and also among the employees create the congenial work environment in organization.
2. The knowledge of organizational behavior helps managers know individual employees and motivate employees work for better results. It helps managers apply inappropriate motivational techniques in accordance to the nature of individual employees who exhibit glaring differences in many aspects.
3. One of the basic characteristic is that it is human in nature, so to say. Organize your behavior tackles human problems humanely. It helps understand causes of problems. Predicts future course of action. Thus, treating employees as human beings enables the managers to maintain cordial industrial managers, which in turn creates peace and harmony in the organization.
4. The most important reason to study organizational behavior is to learn how to predict human behavior and then apply it in some useful way to make the organization more effective.
5. All organization are run by men. It is man forming in the organization makes all the difference. That it implies the effective utilization of people guarantees success of the organization. Organizational Behavior. Health Manager. How to efficiently manage human resources in the organization. It enables managers to inspire managers and employees towards higher productivity and better results.
Models of organizational behavior.
Models are framework or possible explanation why do people behave as they behave at work?
All the models of organizational behavior are broadly classified into four types.
1. Autocratic model.
In case of an autocratic model. The managerial orientation is dictorial. Max Weber defines power as. The probability that one actor within a social relationship will be in a position to carry out his own will, despite the essential features of this model are:
1. Organization with an autocratic environment is autocratic oriented. This authority is delegated by the right of command over the people to whom it applies. The management believes that it’s is the best judge to determine what is better for the health of both the organization and its participants and that the employees obligation is to follow orders. It assumes that the employees have to be directed, persuaded and pushed into performance.
2. Under autocratic model, the employees orientation is obedience to the boss. They did not be respectful to him. The bosses have absolute power to hire Fire and Prosper Fire employees.The employees depend upon the boss and are paid minimum wages for minimum performance.
2. The custodian model.
To overcome the shortcomings of the autocratic model, the custodian model came into existence. The insecurity and frustration filed by the workers under the autocratic model sometimes lead to aggression towards the boss and their family. To dispel this feeling of insecurity and frustration, that need was felt to develop a model which will improve the employer employee relation. Some of the feature of this model are.
1. The success of this model depends upon the economic resource. Because this model emphasizes the economic rewards and benefits.
2. The employees under this model depend upon organization, then their boss. If the organization has got good welfare and development programs for the employee, the employees cannot offer to Leave the organization.
3. Under this model, the employees are satisfied and happy, but they are not strongly motivated.
3. The supportive model.
This model is founded on leadership, not on money or authority. In fact, it is the managerial leadership style that provides an atmosphere to help employees grow and accomplish their tasks successfully. The managers recognize that the workers are not by nature and passive and disinterested in organizational needs, but they are make so by an improve leadership style. The managers believed that given due and approach changes the workers become ready to share responsibility, develop a Devine to contribute towards the organization and improve themselves. Thus, under supportive approach, the management orientation is to support the employee’s job performance for making both organization and individual goals.
4. The collegial model.
This is an extension of the supportive model.
Features of this model.
1. This model creates the favorable climate in the organization. As the workers, they feel that they are partners in the organization.
2. These models inculcates the team spirit in an organization. The workers accept responsibility because they find it their obligation to do so, not because they will be punished by the management.
3. Under this model, the workers have job satisfaction, job involvement, job commitment, and some degree of fulfillment.
4. This model is specially used for research laboratories and similar work situations.
Unit 2
Personality.
The English word personality derived from the Latin word personaire. It means to speak through. Originally, the term denoted the mask worn by the actors in the ancient Greek dramas. In this way, personality is used in physical attractiveness. However, forgiving personality in terms of external appearance is in a narrow sense. Personality includes something more.
Personality may be understood as the characteristic pattern of behavior and modes of thinking that determine a person’s adjustment to the environment.
Thus, it reflects from the above definitions that the opportunity includes both internal and external aspects involved. Here external aspect refer to height, weight, color and other physical traits, 1 attitudes, values, learning etcetera Are the internal aspects of personality.
Determinants of personality.
1. Heredity.
It refers to those factors that are determined at conception. Heredity refers to the biological factors. It is the transmission of qualities from the parents to children through a biological. Physical , muscle composition , facial are example of heredity characteristics.
2. Environments.
The environment that is once early conditioning the family, norms, friends and social group Exert pressure on one personality formation. Culture establishes the norms, attitudes, and values that are passed along from generation to generation. Evidences are available to believe that the cultural environment in which people are raised plays a major role in shaping personality.
Home environment generated to a child also exerts important influence in shaping his or her personality.
Research studies have also revealed that parents have more effect on the personality development on their children as compared to other members of the family.
3. Situation.
Situational factors also plays a very important role in determining personality of a person. Situation in fact exerts an important pressure on individual to behave in a particular manner. In certain cases, how one will behave is not determined by what kind of person is 1 is, but by in which kind of situation one is placed.
4. Social.
Socialism is a process by which an infant acquires from an enormously wide range of behavioral potentialities that are open to him on her, about those behavior patterns that are customary and are acceptable to the family and social groups.
Initially, socialism starts with the contact of the infant with the mother when he or she grows up. Contacts with the other members of the family and social groups influence his or her socialism process. The social groups include school mates, friends, colleagues at workplaces, groups to which an individual belong, etcetera.
Unit 2





intellectual














































Unit 3 4 5






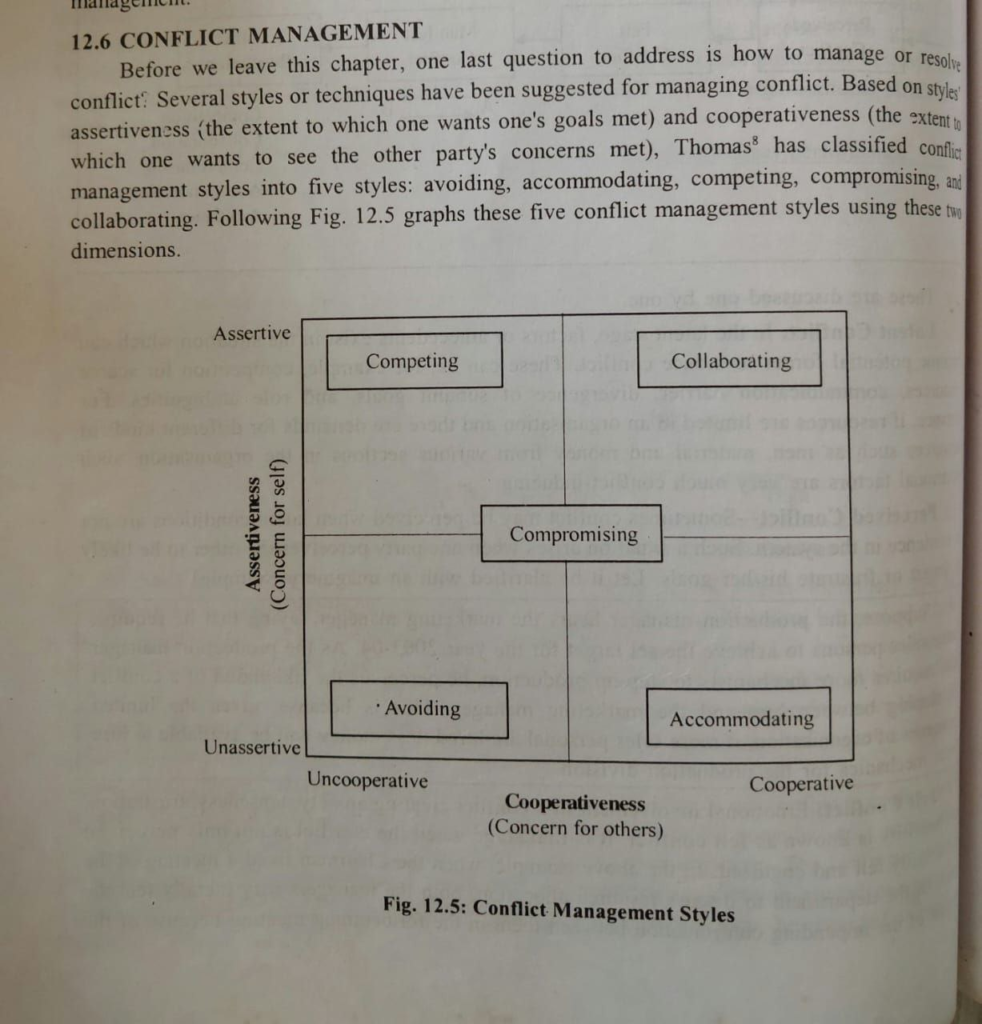









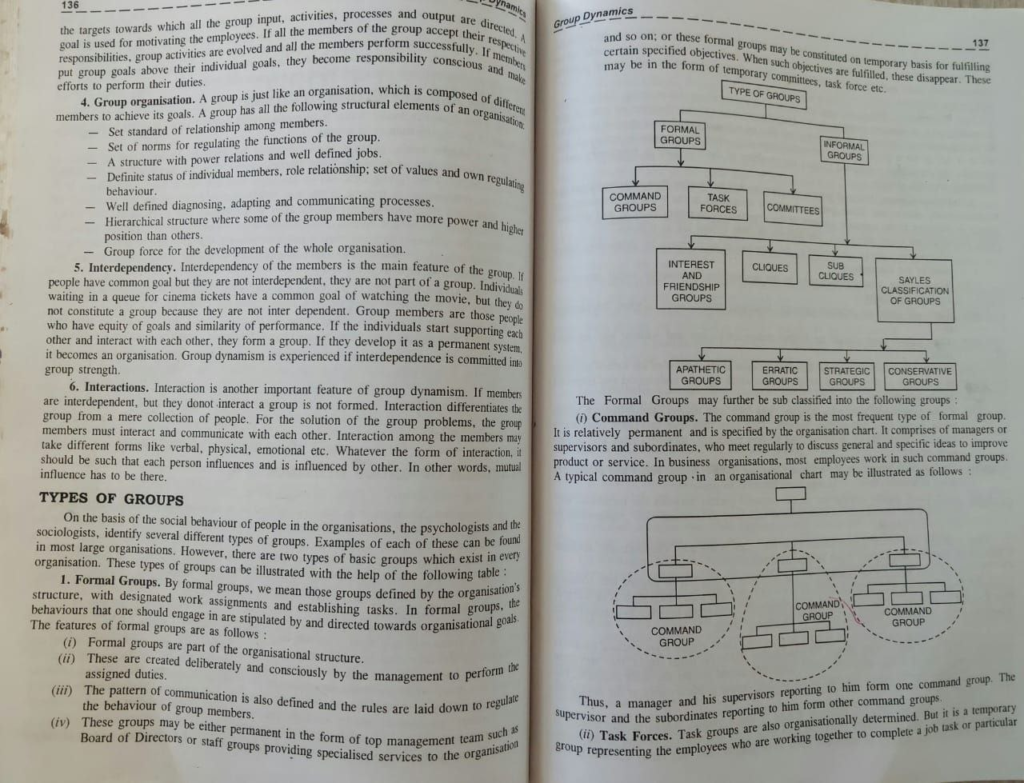







Its like you read my mind You appear to know so much about this like you wrote the book in it or something I think that you can do with a few pics to drive the message home a little bit but other than that this is fantastic blog A great read Ill certainly be back.