Unit 1
Meaning and Definition of Marketing.
Marketing is typically seen as the task of creating, promoting and delivering goods and services to consumers and businesses.
Marketing has been defined in many ways.
According to the Committee of Marketing Teacher’s Association, USA, “Marketing is the performance of business activities that direct the flow of goods and services from producers to consumers or users.”
According to Philip Kotler, “Marketing is a societal process by which individuals and groups obtain what they need and want, through creating, offering and freely exchanging products and services of value with others.”
According to Paul Mazur, “Marketing is the delivery of a standard of living to the society.”
Thus, marketing is the creative management function which promotes trade and employment by assessing consumer needs and initiating research and development to meet them. Marketing makes goods and services useful to the society by getting them where they are wanted, when they are wanted and by transferring them to those people who want them. In this sense marketing means, “All the activities involved in the creation of place, time and possession utilities.” It has been righty remarked, “Nothing happens in our economy until somebody sells something.”
Nature of Marketing
When we discuss the nature of marketing we come to know that marketing is both a science as well as an art. It has the features of both science as well as art.
Marketing as a science:
The handling of marketing responsibilities needs a diversity of human talents. These responsibilities require the men who have personality traits which enable them to do an effective job in dealing with customers.
Marketing needs innovative and imaginary people to create effective advertisement and sales promotion programmes. Marketing people need to develop new ideas in products, market and distribution methods. They must have strong analytical abilities and observations to cope with the strategical and logistical aspects of marketing operations.
All these prove that marketing is a science. Many marketing problems can be sorted out by taking a scientific approach.
Marketing as an art:
Marketing is a continuous practice through which one can bring perfection. Marketing develops a ‘group of artists’ for bringing solutions to the problems of personal selling, advertising and sales promotion etc. The artistic aspect of marketing influence and educate the customers and bring success to the organization.
As science and art, the nature of marketing has the following features-
| As Science | As an Art |
|---|---|
| 1. It advances knowledge | 1. It advances practice |
| 2. It proves | 2. It feels |
| 3. It predicts | 3. It guess |
| 4. It impresses | 4. It expresses |
| 5. It measures | 5. It opines |
| 6. It defines | 6. It describes |
Scope of Marketing
Marketing is typically seen as the task of creating, promoting and delivering goods and services to consumers and businesses. Marketing people are involved in marketing of ten different types of entities. In other words, marketing today includes the following activities within its scope –
1. Goods:
Physical goods constitute the bulk of most countries production and marketing efforts. For example, each year US companies alone market billions of canned and frozen goods, million tons of steel, cars, tv sets, machines etc.
2. Services:
As economies advance, a growing proportion of marketers’ activities are focused on the production of services. Services include the work of airlines, hotels, beauticians, maintenance and repair people as well as professionals such as accountants, lawyers, engineers, bureaucrats, doctors, software programmers and management consultants.
3. Experiences:
By producing several services and goods, a firm can create stage and market experiences. Walt Disney World’s Magic Kingdom represents experiential marketing. Customers visit a fairy kingdom or a haunted house. There is also a market for customized experiences, such as spending a week at a baseball camp playing with some retired baseball greats or climbing Mount Everest.
4. Events:
Marketers promote time-based events, such as Olympics, company anniversaries, major trade shows, sports events and artistic performances. There is a whole profession of meeting planners who work out the details of an event and make sure it comes off perfectly.
5. Persons:
Celebrity marketing is a major business. Today every major film star has an agent, a personal manager and ties to a public relations agency. Artists, musicians, CEOs, physicians, lawyers and other professionals are also getting help from celebrity marketers.
6. Places:
Places i.e., cities, states, regions and whole nation compete actively to attract tourists, factories, company headquarters. For example – Ireland has been an outstanding place marketer having attracted more than 500 companies to locate their plants there.
7. Properties:
Properties are intangible rights of ownership of either real property or financial property. Properties are bought and sold, and this requires marketing. Investment companies and banks are involved in marketing securities (financial property) to both institutional and individual investors.
8. Organizations:
Organizations actively work to build a strong and favorable image in the minds of their target customers. Companies spend money on Corporate Identity Ads. Universities, museums and performing art organizations all use marketing to boost their public images and to compete for audiences and funds.
9. Information:
Information can be produced and marketed as a product. We buy software and CDs and we visit internet for information. The production, packaging and distribution of information are one of the society’s major industries.
10. Marketing of Ideas:
Every market offering includes a basic idea. Charles Revson of ‘Revlon’ observed, “In the factory we make cosmetics, in the store we sell hope.” Products and services are platforms for delivering some idea or benefits. Today social marketers are busy in promoting ideas such as –
a) Say no to Drugs,
b) Save the Rain Forest,
c) Exercise Daily,
e) Avoid fatly food.
Importance of Marketing
The various functions of marketing under concentration, equalization and dispersion are explained below with their importance –
1. Buying and Assembling:
Buying and assembling is an important function of marketing. The marketers have to take a number of decisions regarding the types of products to be purchased or assembled. Their quality, quantity, price, time of purchase, selection of suppliers and forms of purchase.
The failure in the successful performance of buying function may lead to losses in the form of unsellable inventories, which will finally be the cause of business ruin.
2. Selling:
Selling creates demand for a product.
Selling function includes –
a) Product planning and development.
b) Finding out the buyers.
c) Creation of demand through personal selling, advertisement and sales
promotion.
d) Negotiation of terms of sale.
e) Sales contract.
Selling is important not merely for increasing the profits but also for making the goods and services available to the consumers in the society. In modern marketing selling activity involves tackling with a number of problems such as facing competition and conducting market research from time to time.
3. Standardization and Grading:
Standardization and grading are also important functions of marketing. Standardization is the process of setting up standards. It assures quality. It promotes uniformity of products i.e. size, shape, design and colour of the products. Grading is a part of standardization. It is a process of sorting out goods into a number of grades or classes. Grading enhances marketing efficiency.
4. Financing:
Financing is the life blood of business. Value of goods is expressed in money and it is denoted by price to be paid by a buyer to a seller.
Finance is very important in marketing operations such as maintenance of minimum inventory level, payment of rent and insurance charges. Salaries and commission to sales force, advertising expenses etc.
5. Warehousing and Storage:
The place where the goods are stored and
preserved against natural and human hazards is known as warehouse.
Warehousing and storage of goods are necessary not only for the markets but
also for the wholesalers (as well as) and retailers.
Warehousing performs the functions like, storage risk bearing, price
stabilization, packing etc.
6. Marketing Risk (Risk taking):
Risk is a universal function and is present in all marketing transactions. Risks are constantly challenging the businessmen and no businessmen are able to develop an all-out formula to eliminate risk 100%.
Risk implies an element of uncertainty and possibility of loss due to some unpredictable happening of events in future. There are many ways of minimizing risk. They may be –
a) Avoiding or preventing the risk
b) Shifting the risk (insurance)
c) Accepting unavoidable risk
7. Marketing Information:
Marketing conditions are dynamic and they may affect industry in any way and to any degree. Therefore, marketers must know the trends in marketing demand, supply, prices, competition and other related marketing information.
8. Transportation:
Transportation involves the movement of goods from the point of production to the point of consumption. Without transportation, large scale production, specialization and distribution would have become impossible. Transportation provides place utility to products. The marketers need to use the appropriate mode of transport for quick and safe movement of goods at the minimum possible cost.
Marketing Concepts
Marketing concept means the philosophy which guides the marketing efforts. There are marketing concepts which are adopted by organizations for their marketing activities. They may broadly be divided into two groups-
Traditional Concept
Production Concept
Product Concept
Selling Concept
Modern Concept
Marketing Concept
Societal Marketing Concept
1. The Production Concept:
This concept holds that the consumers will support those products that are produced in large quantities at low unit cost. The authorities of this view believe that marketing can be managed by managing production. It involves high production efficiency and wide distribution network. This concept holds good (valid) in cases where there is more demand than supply. In such a situation, consumers readily accept the product that is made available. For e.g. cooking gas.
Production ——-> Consumption
2. The Product Concept:
Under this concept, producers believe that if the product is good and reasonably priced, it will be quite popular among consumers even if no special marketing efforts are made. They are of the opinion that it is the quality of product alone will yield satisfactory sales. The marketers under this concept believe on the slogan that, “Good wine needs no wishes.”
Production —> Quality of Product —> Consumers
3. The Selling Concept:
The third concept followed is the selling concept. Under this concept it is presumed that consumers will not normally buy as much as expected unless they are approached and convinced. The company lays emphasis on getting sufficient sales for its products. Under this concept the company assumes that its products are sold and not bought. In other words, the consumer’s satisfaction is considered secondary, selling the product is the primary consideration. Till 1953, marketing was usually sales oriented.
Production —> Product Quality —> Approaching Consumer’s —> Consumers
4. The Marketing Concept:
This is a new idea in the field of exchanging. Under this concept, the organization tries its best to determine the needs, wants and values of the buyer’s market and finally takes all steps to deliver the desired satisfaction more effectively and efficiently than its competitors do. Every attempt is made to satisfy the wants of customers. Winning the confidence of customers is as good as fulfilling the goals of organization. In selling, the main idea is to convert the product into cash. But marketing deals with the satisfaction of the customers with the product that is supplied. Marketing concept has been extensively adopted.
Identification of needs
⬇️
Production
⬇️
Product Quality
⬇️
Selling Efforts
⬇️
Satisfaction of the Consumers Needs
5. Societal Marketing Concept:
Under the marketing concept, individual satisfaction and personal interest are both ignored. This limitation is removed by introducing the societal marketing concept. This concept aims at giving individual satisfaction so far the costumer is concerned and maintains public welfare as its goal and responsibility in the long run. The societal marketing concept involves creation of a healthy life for its customers by providing quality products and maintaining customer interest at the top level.
The societal marketing concept believes in the slogan that, “Marketing both begins and ends with the customers.”
This is the current or modern concept which has been extensively adopted and widely accepted in the interest of the organization, the customers and the society. In short, societal marketing can seek profits by-
a) Satisfying customer utility.
b) Maximizing the public welfare.
c) Enhancing the quality of life.
Difference between Selling and Marketing
| Basis | Selling | Marketing |
|---|---|---|
| 1. Objective | Its main objective is to maximize sales without caring for the needs and satisfaction of the customers. | Its main objective is to identify the wants and demands of the buyers and to satisfy them. |
| 2. View | It views business as a process of converting finished goods into turnover. | It views business as a value satisfying process. |
| 3. Cost and Price | In selling, cost determines price. | In marketing, price determines cost. |
| 4. Decision of Production | In selling, seller determines what product or service is to be produced. | In marketing, buyer determines what they want and what product or service is to be produced. |
| 5. Goal | It tries to maximize the profits by converting output into cash. | It tries to maximize profits by satisfying consumer needs and delivering quality of life to people. |
| 6. 4 Ps | In selling, the decisions on ‘Four Ps’ i.e., Product, Price, Place and Promotion are taken from seller’s point of view. | In marketing, decisions on ‘Four Ps’ are taken from customers’ point of view. |
Marketing Environment
Marketing environment comprises external or macro factors over which
the organization and management has little control. These are relatively
uncontrollable external forces.
The marketing management must be in close contact with many
uncontrollable forces. To be successful in marketing they must learn to
accommodate them and if possible to take advantage of them. These
uncontrollable forces are the parameters of the market.
Let us describe the various environmental forces of marketing in brief:
| Forces | Components of the Environment |
|---|---|
| 1. Socio-cultural | Changes in social values, lifestyles, role of women, attitudes, preferences etc. |
| 2. Technology | Innovation of new technology, product innovation, distribution, packaging etc. |
| 3. Economic | Economic growth, economic policy and stability, per-capita income, economic system etc. |
| 4. Political-legal | Stability of government, law, political organizations, foreign policy, consumer protection. |
| 5. Demographic | Population growth, age, sex, level of education, density of population etc. |
| 6. Competing firms | Substitute brands, competitive firms, price policy etc. |
| 7. Ecological | Air, water and noise pollution, conservation of forests and scarce resource |
1. Socio-cultural factors:
The socio-cultural environment determines the value system of a society. Marketing manager is called upon to make necessary adjustments in marketing policies and strategies in order to meet the socio-cultural needs of people.
There are three aspects of socio-cultural environment.
a) Changes in our lifestyle and social values.
b) Growing consumerism indicating consumer dissatisfaction since 1960.
c) Major social problems i.e. concern for pollution of our environment.
We have witnessed many changes in socio-cultural environment in India. Indian consumers are acquiring new lifestyles influenced by various satellite channels. There is a clear decline in joint family concept in favour of nuclear family.
2. Technological factors:
Technology has shaped the face of human life faster than the pace of human life. The unprecedented development of science and technology has created a phenomenal impact on our lives. We have witnessed radical changes in our lifestyles, in our consumption pattern as well as in our economic welfare.
The technological changes have increased competition in the market and the marketers are compelled to innovate and improve the products. The packaging technology has revolutionized the Indian Industry. The world has moved from early machine age to the digital age.
3. Economic factors:
Marketing plans and programmes are influenced by many economic factors like economic growth rate, level of employment and income, purchasing power and willingness to buy, price level, interest rate,consumer credit etc. The role of marketing management becomes important when economic factors greatly touch the lives of consumers. The liberalization of economic policies is responsible for bringing changes in our economic system, economic policies, licensing policy, investment policy, merger and acquisition policy etc. For e.g. Coca-Cola had to go from India in 1977. But in 1992 it came back due to changes in economic policies.
4. Political and legal forces:
Political and legal forces are gaining considerable importance in marketing activities and operation of business enterprises. Marketing system is affected by government, monetary and fiscal policies, import/export environment influence marketing plans and policies. E.g. the bio-medical waste rules 1998 apply to all persons to generate, collect, receive, store, transport, dispose or handle the bio-medical waste in any form.
5. Demographic forces:
Demographic environment refers to the development of population growth, age, sex, education pattern, urban and rural population, occupation, income etc. The demographic factors are directly related to the marketing activities. Hence, management must make a scientific study of human population and its distribution structure.
E.g. growing population indicates growing marketing particularly for baby products. But, when we have reduction in the birth rate and the lower rate of growth of population, companies, specializing in baby products will have to adjust their marketing program accordingly.
6. Competitive environment:
No marketing decision of major importance should be made without accessing competition in a free market economy. The marketing manager has little or no control over activities of competitors. Competitor’s considerably influence the marketing strategies particularly in relation to selection of target market, suppliers, channels of distribution, product mix, price mix and promotion mix.
Competition may be of two types:
a) Competition within an industry producing and selling similar goods.
b) Competition between two companies engaged in production and selling of different goods or services. The marketing manager must understand that his rivals are bound to limit the marketing activities of his firm sooner or later.
7. Ecological factors:
Ecological environment has assumed a unique importance in production and marketing in modern economies. The marketers are expected to take measures to conserve and allocate scarce resources properly. Prevention of all types pollution and efficient use of scarce resources can restore the balance in our ecological environment. The marketers have to innovate new marketing process so as to make them eco-friendly.
Marketing Mix
The policies adopted by manufacturers to attain success in the market constitute the marketing mix. Broadly speaking, the combination of marketing methods or device is known as marketing mix.
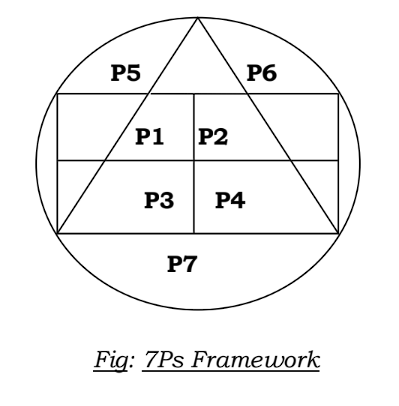
There are 7 Ps in the marketing mix. They may broadly be divided as:
A) Traditional Marketing Mix:
It consists of 4 Ps i.e. product, price, place and
promotion.
B) Extended Marketing Mix:
It consists of 3 more Ps people, process and
physical evidence.
The 7 Ps in marketing are known as elements of Marketing Mix. They are
explained below:
A. Traditional Marketing Mix:
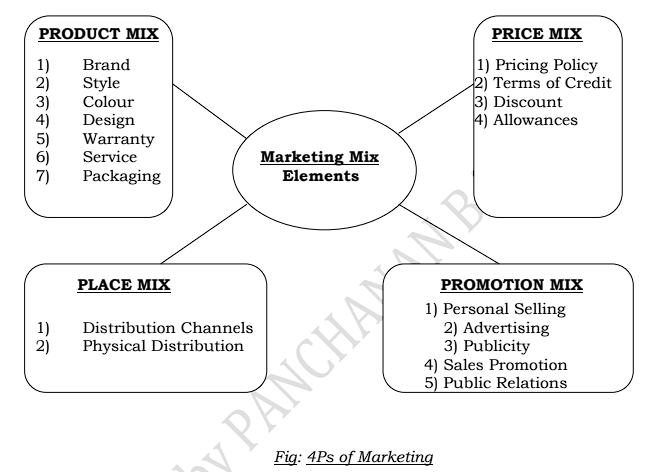
1. Product Mix:
Product is the thing possessing a bundle of utilities. It covers
the physical attributes, the package, branding, labelling, style, shape and
design, warranties and after sales services of the product. The product mix
must match with customer needs and expectations.
2. Price Mix:
It includes pricing policies and pricing objectives. Price is the
monetary value of the product. Pricing decision also includes discount,
allowances, terms of credit, profit margin etc. Price is an effective means of
publications. It can also act as a device of promotion.
3. Place Mix:
Place mix covers decisions about-
i) Channels of distribution including all middlemen and facilitating agencies and
ii) Physical distribution which is concerned with transporting, warehousing, storing and handling of products.
4. Promotion Mix:
It covers all means of marketing communication designed to persuade buyers to purchase the product. There are five main devices of promotion:
a) Personal selling
b) Advertising
c) Sales promotion
d) Publicity
e) Public relations
B. Expanded Marketing Mix:
In 1988, 4Ps concept was challenged by Alan. J. McGrath. He added three more Ps to the traditional 4Ps and suggested ‘7Ps’ framework of marketing mix.
The 3Ps include:
1) People
2) Process
3) Physical evidence
The 3 Ps are explained below:
5. People:
People mean those who are in touch with the consumers i.e. salesmen. They deliver the services to the consumers. People in service marketing must possess sound knowledge and skill and they must have positive attitude towards the customers.
6. Process:
Process means the system or method used by the marketers for delivering the goods and services to the customers. The process must be customer friendly. In modern marketing all companies are trying to have some comparative advantages over the others in developing the process.
7. Physical Evidence:
It includes use of vouchers, cards, booklets etc. which are of use to the customers as evidence of visiting that place or institution. It also includes the maintenance of neat and clean shopping area with sufficient space for parking and sitting arrangements. The place where delivery and service of product takes place must be entertaining with beautiful interior decorations.
Market Segmentation
Market segmentation is a marketing strategy that involves dividing a target audience into groups based on shared characteristics. The goal is to create more targeted products and advertisements that appeal to specific groups, which can lead to higher returns on investment (ROI).
What are the basis of market Segmentation
Bases for Segmenting Consumer Market
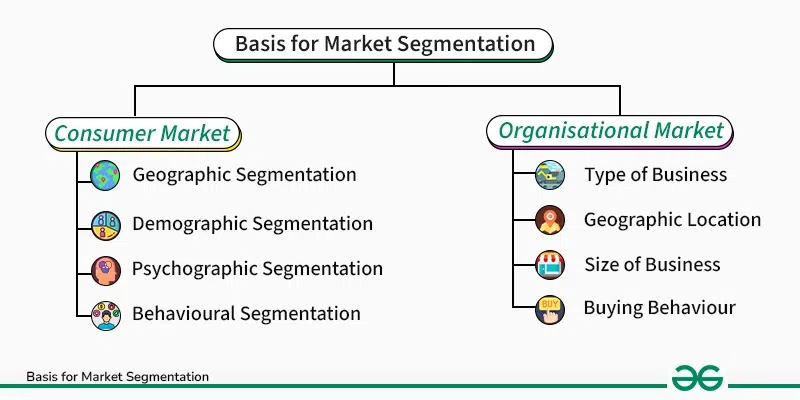
Major bases for segmenting the consumer market include geographic, demographic, psychographic, and behavioural variables.
1. Geographic Segmentation:
Geographic segmentation calls for dividing the whole consumer market into different geographical units such as nations, regions, states, cities, etc. A company may want to target one or more geographical units but should pay attention to the differences in needs and wants of different units. Various factors, like geographical conditions, cultural influence, etc., help identify the various geographic segmentations.
Example: McDonald’s offers a range of vegetarian options in India, including the McAloo Tikki Burger.
2. Demographic Segmentation:
Demographic segmentation involves segmenting the market according to various basic yet important factors. Factors like age, gender, income, etc., determine the segments under demographic segmentation.
Example: Coca-Cola segments its market according to various demographic factors and formed segments like the youth market and health-conscious adults.
3. Psychographic Segmentation:
This type of segmentation includes dividing the whole consumer market into various segments based on personality and lifestyle. Personality refers to the combination of various characteristics like traits, habits, attitudes, etc. Lifestyle includes how an individual lives and spends their money and time.
Example: Apple’s marketing and product design are known for appealing to customers who value innovation and creativity.
4. Behavioural Segmentation:
Behavioural Segmentation involves segmenting the market into various segments based on how an individual reacts in a certain situation or to a particular product/service.
Example: Amazon uses behavioural data to personalise product recommendations for its customers.
Bases for Segmenting Organisational Market
Major bases for segmenting the organisational market include the type of business, geographic location, size of business, and buying behaviour.
1. Type of Business:
Organisational market segmentation can be done based on the type of business. There are various sectors in the economy, the demands of which can differ from one another. Sectors like agriculture, mining, communication, services, construction, etc., need different types of technology and functions.
Example: Microsoft’s cloud computing service, Azure, offers industry-specific solutions.
2. Geographic Location:
Organisational segmentation can be done on the basis of the location of the buying business. Different locations have different weather, culture, lifestyle, etc. On the basis of these factors, businesses decide to target one or more segments.
Example: Coca-Cola offers its beverage portfolio to suit regional tastes and preferences.
3. Size of Business:
The size of the buying business can also affect the segmentation strategy. Businesses can be small, medium-sized, and large-sized. Medium and large-sized businesses are given more preference over small-sized businesses.
Example: Oraofferscle, a provider of enterprise software solutions, offers different product lines based on the size and complexity of businesses.
4. Buying Behaviour:
Organisational market segmentation can be done on the buying behaviour of a business. Business buying behaviour can include new buyers, modified buyers, and repeat buyers.
Example: Amazon Business, a B2B marketplace, offer features like bulk pricing, business-only selection, and multi-user accounts.
Define Product
A product is the item offered for sale. A product can be a service or an item. It can be physical or in virtual or cyber form. Every product is made at a cost and each is sold at a price. The price that can be charged depends on the market, the quality, the marketing and the segment that is targeted.
Various Stages of PLC
The product life cycle is the succession of stages that a product goes through during its existence, starting from development and ultimately ending in decline. Business owners and marketers use the product life cycle to make important decisions and strategies on advertising budgets, product prices, and packaging.
In the marketing industry, the typical depiction of the product life cycle only has four main stages — Introduction, Growth, Maturity, and Decline.
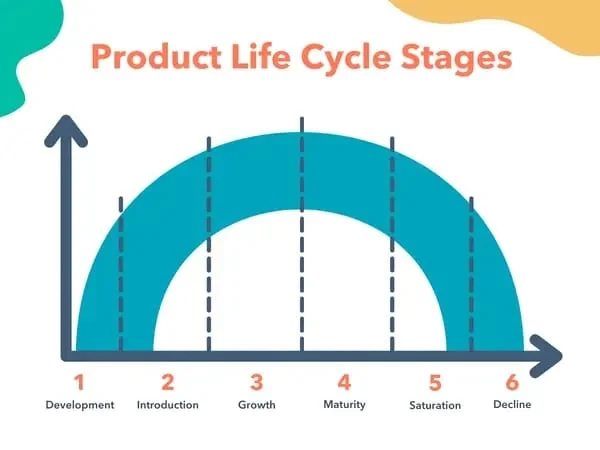
1. Development
The development stage of the product life cycle is the research phase before a product is introduced to the marketplace. This is when companies bring in investors, develop prototypes, test product effectiveness, and strategize their launch.
In this stage, companies typically spend a lot of money without bringing in any revenue because the product isn’t being sold yet.
This phase can last for a long time, depending on the complexity of the product, how new it is, and the competition. For a completely new product, the development stage is particularly difficult because the first pioneer of a product isn’t always as successful as later iterations.
Before full-scale production, the product may be released in a limited market or region for testing purposes. This allows companies to assess market acceptance, gather user feedback, and make necessary adjustments before a wider launch.
2. Introduction
The introduction stage happens when a product is launched in the marketplace. This is when marketing teams begin building product awareness and targeting potential customers. Typically, when a product is introduced, sales are low and demand builds slowly.
In this phase, marketers focus on advertising and marketing campaigns. They also work on testing distribution channels and building product and brand awareness.
This stage is crucial because companies have the opportunity to shake up the status quo and capture the attention and loyalty of early adopters. The positive experiences and word-of-mouth recommendations from these early customers can influence the broader target market and accelerate product adoption.
Some examples of products currently in the introduction stage include:
Generative AI
Self-driving cars
3D televisions
Ultimately, the success of this stage sets the foundation for the product’s future growth and success in subsequent stages of the product life cycle.
3. Growth
During the growth stage, consumers have accepted the product in the market and customers are beginning to truly buy in. That means demand and profits are growing, hopefully at a steadily rapid pace. This momentum is crucial for sustaining business operations, funding further product development, and generating returns on investment.
As companies scale, they can benefit from lower per-unit production costs, improved supplier relationships, and optimized distribution networks.
However, there are some challenges that come with the growth stage. As the market for the product expands, competition grows. Potential competitors will see your success and will want in.
Some products that are currently in the growth stage are:
Smartwatches
Electric cars
Peloton
During this stage, it’s important to keep attracting new customers and solidify your brand image so you can stay ahead of the competition.
4. Maturity
The maturity stage is when the sales begin to level off from the rapid growth period. At this point, companies begin to reduce their prices so they can stay competitive amongst the growing competition. Streamlining production processes, negotiating favorable supplier contracts, and optimizing distribution networks also become important considerations.
This is the phase where a company begins to become more efficient and learns from the mistakes made in the introduction and growth stages. Marketing campaigns are typically focused on differentiation rather than awareness. This means that product features might be enhanced, prices might be lowered, and distribution becomes more intensive.
During the maturity stage, products begin to enter the most profitable stage. The cost of production declines while the sales are increasing.
Examples:
Smartphones
Amazon
Video game consoles
5. Saturation
During the product saturation stage, competitors have begun to take a portion of the market and products will experience neither growth nor decline in sales.
Typically, this is the point when most consumers are using a product, but there are many competing companies. At this point, you want your product to become the brand preference so you don’t enter the decline stage. To achieve this, you’ll want to focus on providing exceptional service and building strong relationships with your customers.
In a saturated market, innovation also becomes essential to stay relevant. Businesses must continuously invest in research and development to improve products and offer new features. Failure to do so may lead to product obsolescence and loss of market share.
Some examples of products in the saturation stage are:
Streaming services
Breakfast cereals
Soft drinks
6. Decline
Unfortunately, if your product doesn‘t become the preferred brand in a marketplace, you’ll typically experience a decline. Sales will decrease during the heightened competition, which is hard to overcome.
Decline also occurs when products become outdated or less relevant as newer technologies enter the market. Consumers may turn to more advanced options, rendering the declining product less desirable.
If a company is at this stage, it’ll either discontinue its product, sell the company, or innovate and iterate on its product in some way.
Here are a few examples of products in the decline stage:
CDs and cassette tapes
Landline telephones
DVDs
The best companies will usually have products at several points in the product life cycle at any given time. Some companies look to other countries to begin the cycle anew.
What is new product development
New product development (NPD) is the process of creating a new product, service, or technology for the market. It’s a complex, iterative process that involves multiple stages, from idea to launch, and requires the participation of many different departments
Various stages of New Product Development
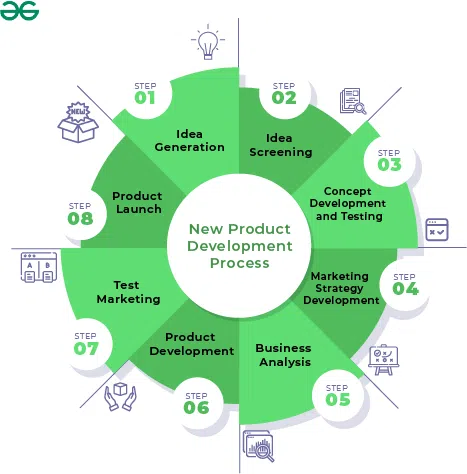
When a company develops a new product, it cannot just hope that the product will be a success in the market. It is essential for the company to understand its customers, markets, and competitors before developing a product to deliver superior value to customers. For this, the company must carry out a strong new product development process. The eight major steps of the new product development process are as follows:
1. Idea Generation
Idea generation refers to brainstorming new product ideas or strategies to innovate an existing product. The different internal and external sources through which a company generates ideas for a new product are customers, distributors, suppliers, competitors, etc. Before creating any product, companies evaluate market conditions, perform studies, understand the users’ wants and needs, and then suggest possible solutions. SWOT analysis is a very effective technique to discover the weak aspects of the product as well as to explore where significant opportunities exist. A SWOT Analysis is a framework to evaluate the organisation’s Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, and Threats. At last, this stage aims to generate as many ideas as possible which are feasible and deliver value to consumers. The need for high-quality photography among consumers, for instance, can inspire a mobile phone maker to develop the idea of a smartphone with a novel camera system.
2. Idea Screening
The second stage is called Idea Screening. This stage involves screening and reviewing all of the ideas generated in the first step and selecting only those with the best probability of success. Many factors are kept in mind while deciding which ideas to accept and which to reject. These factors include projected advantages to consumers, necessary product innovations, technical viability, and feasibility for marketing. The stage of idea screening is best performed within the company. Experts from several teams also assist the company in assessing the requirement of resources, the need for technology, and the marketability of the proposal. For instance, an automobile manufacturer may evaluate potential concepts for electric vehicles before manufacturing electric cars while considering factors, like the availability of batteries, their affordability, and how well they would appeal to consumers.
3. Concept Development and Testing
After all the ideas pass through the stage of idea screening, these ideas are evolved into concepts. A product concept is a detailed version of the product idea and contains a precise explanation of the idea. It should highlight the target audience, the pricing for the product, and the characteristics and advantages of the product that could be valuable for the customers. Generating various product concepts assist the companies in determining how attractive each concept is to buyers and selecting the one that will bring them the most value. Once the concepts are generated, they are tested within a select group of consumers. Concept testing is a great technique for validating product ideas with users before committing time and resources to develop them. For instance, any business producing sportswear products might create a concept for a light running shoe and seek opinions from athletes concerning the product’s comfort, toughness, and design.
4. Marketing Strategy Development
Once a concept is selected and well-validated, it is essential to develop a preliminary marketing strategy to launch the product to the market based on the product concept and assess the worth of the product from a business point of view. The marketing strategy helps in deciding pricing, positioning, and promoting the product. A marketing strategy statement includes three parts:
The first part of the statement describes the target market, the firm’s planned value proposition, and its sales, market share and profit goals for the first few years.
The second part of the statement includes the product’s planned price, its distribution, and marketing budget for the first year.
The last part of the statement consists of the planned long-run sales, marketing mix strategy, and profit goals.
Once the marketing strategy has been developed, product management can assess the economic desirability of the product.
5. Business Analysis
Once the marketing strategy has been developed it is important to assess the worth of the product from a business point of view. An assessment of the sales projections, estimated expenses, and anticipated profits are included in the business analysis. And, If they meet the goals of the company, the product can proceed to the product development stage. For instance, a food company would assess the profitability of a new snack by looking at the expenses associated with ingredient sourcing, production, packaging, and distribution.
6. Product Development
The next stage is Product Development. In this stage, the R&D or engineering department converts a product concept into a physical product. This step involves a huge jump in investment as it shows whether or not the product idea can be turned into a workable product. The R&D Department tries to design a prototype to satisfy customer needs and excite them in buying the product, and can also be produced quickly and within budget. For this, the department runs tests on one or more physical versions of the product concept. Development of a successful prototype may take time (days, weeks, months, or even years). The companies can do product testing on their own or can outsource testing from a third party/firm which specialises in testing. For instance, a tech business might create test versions of a new smartwatch, evaluate how well it works, and then make design changes that can satisfy the customer’s needs.
7. Test Marketing
The next step is Test Marketing. Test Marketing refers to the process of testing the product and marketing program in realistic market settings. With this step, the marketer can have the experience of marketing the product in the market at a small scale before spending huge money on its full introduction. Simply put, test marketing lets the organisation test its product and its marketing program including targeting, positioning strategy, distribution, advertising, branding, pricing, packaging, and budget levels.
The cost of performing test marketing can be high, and as it takes time, it can give The need for test marketing and the level of test marketing varies with the product. When the cost of developing and introducing the product is low, or when the management is confident about the product’s success, the company may do no or little test marketing. However, when the introduction of a new product requires a big investment, risks are high, or when the management is not confident about the product and its marketing program, it may do a lot of test marketing. For instance. a cosmetics company might launch a new skincare product in a particular area and collect information on consumer reaction, usage trends, and sales.
8. Product Launch
At the final stage, companies are now prepared to launch the new product onto the market. For a successful launch, a company must ensure that the product, marketing, sales, and support teams are well-placed and should keep good track of its performance. Companies must frequently monitor and evaluate the success of the product launch and make modifications if it fails to accomplish the expected goals. For instance, a software provider might monitor sales, client feedback, and user satisfaction polls to assess the effectiveness of a recently introduced productivity tool.
Define Brand
A brand is the perception or identity that a company, product, or individual establishes in the minds of consumers. It encompasses the name, logo, design, messaging, and overall experience that differentiates it from others. A brand is more than just a logo or a product; it’s the emotions, associations, and values that customers connect with.
Key elements of a brand include:
Brand Identity: Visual and verbal elements like logos, colors, and taglines.
Brand Image: How the public perceives the brand.
Brand Promise: What consumers expect to receive from the brand.
Brand Values: The principles and ideals the brand stands for.
Brand Loyalty: The attachment consumers develop to a particular brand.
Essentials of a Good Brand Name
A good brand name is crucial for a company’s identity and plays a significant role in attracting and retaining customers. Here are the essentials of a good brand name:
1. Memorability
- The name should be easy to remember and recognize. Simplicity helps consumers recall the brand quickly, making it more likely for them to return.
2. Simplicity
- A short, simple name is easier to pronounce, spell, and understand. Complicated or long names can be confusing and difficult to remember.
3. Uniqueness
- A good brand name stands out from the competition. It should be distinctive and not easily confused with other brands in the same market.
4. Relevance
- The name should reflect the brand’s mission, values, or the products/services offered. It should give some idea of what the business is about or resonate with its target audience.
5. Scalability
- The name should allow for growth, so it remains relevant even if the company expands its product line or enters new markets. It shouldn’t limit future business opportunities.
6. Positive Connotations
- A good brand name carries positive associations and evokes good feelings. It should avoid negative or confusing meanings, especially in different languages or cultures.
7. Adaptability
- The name should be versatile enough to work across different platforms, whether digital (websites, social media) or physical (packaging, signage).
8. Legally Available
- It is essential that the name is not already trademarked or in use by another company. It must be legally available to avoid conflicts and protect the brand.
9. Emotional Connection
- A strong brand name can evoke an emotional response or connection, making it more appealing to customers. Names that tap into customers’ values, desires, or emotions can foster brand loyalty.
10. Consistency with Brand Identity
- The name should align with the overall brand strategy, including the brand’s tone, personality, and positioning. It should fit the image the company wants to project.
Define Labeling
Labeling
Labeling refers to the process of attaching or printing informative labels on a product. These labels typically provide important details about the product, such as its name, contents, ingredients, usage instructions, expiration dates, manufacturer information, and legal warnings. Labeling is a crucial aspect of marketing and regulatory compliance because it communicates vital information to consumers and helps them make informed purchasing decisions.
Key functions of labeling:
- Product Identification: Helps consumers recognize the product.
- Information Provision: Offers details like ingredients, usage, and instructions.
- Legal Compliance: Meets regulatory requirements such as safety warnings or nutritional facts.
- Branding: Conveys brand identity through logos, designs, and messaging.
Define Packaging
Packaging
Packaging is the process of designing and producing containers or wrappers for a product. It serves both practical and promotional purposes, protecting the product from damage during transportation and storage, while also serving as a marketing tool. Good packaging not only preserves the product’s quality but also attracts potential customers through design and functionality.
Key functions of packaging:
- Protection: Safeguards the product from physical damage, contamination, and spoilage.
- Convenience: Makes the product easy to handle, transport, and store.
- Promotion: Serves as a tool to market the product through attractive design, branding, and messaging.
- Differentiation: Distinguishes the product from competitors with unique packaging designs.
- Information: Displays essential product information, much like labeling.
Unit 3
Concept of Product Life Cycle (PLC)
The Product Life Cycle (PLC) is a framework that describes the stages a product goes through from its introduction to its decline in the market.
It helps businesses plan strategies for each stage to maximize profitability and sustainability. The PLC is typically divided into five stages:
1. Development Stage (Pre-launch)
- Description: The product is conceived, designed, and developed. Costs are incurred for R&D, testing, and market research.
- Focus: Product innovation and feasibility.
- Key Challenge: High investment with no revenue as the product is not yet launched.
- Example: Tesla’s development of new electric vehicle models.
2. Introduction Stage
- Description: The product is launched into the market. Awareness and adoption are low, and marketing efforts are intensive.
- Focus: Creating awareness, educating consumers, and stimulating demand.
- Characteristics:
- High promotional costs.
- Limited or no profits due to high expenses.
- Strategies:
- Invest in advertising and distribution.
- Offer promotional discounts.
- Example: Virtual reality headsets when first introduced.
3. Growth Stage
- Description: The product gains acceptance, sales increase rapidly, and profits improve.
- Focus: Expanding market share and establishing a competitive advantage.
- Characteristics:
- Higher revenue and profits.
- Increased competition.
- Reduced marketing costs as brand recognition improves.
- Strategies:
- Add features or variations.
- Expand distribution channels.
- Example: Electric scooters gaining popularity in urban markets.
4. Maturity Stage
- Description: Sales peak and stabilize as the market becomes saturated. Growth slows down, and competition intensifies.
- Focus: Retaining customers and defending market share.
- Characteristics:
- Lower profit margins due to price competition.
- Customers become more price-sensitive.
- Strategies:
- Diversify products (line extensions).
- Focus on customer retention and brand loyalty.
- Example: Smartphones like iPhones and Samsung Galaxy in mature markets.
5. Decline Stage
- Description: Sales and profits decline due to changing consumer preferences, technological advancements, or market saturation.
- Focus: Reducing costs and deciding whether to rejuvenate or phase out the product.
- Characteristics:
- Low demand and revenue.
- Product discontinuation may occur.
- Strategies:
- Offer discounts to clear inventory.
- Explore rebranding or innovation.
- Example: DVDs replaced by streaming services like Netflix.
Importance of PLC
- Helps businesses adapt strategies at each stage.
- Guides investment decisions.
- Identifies the need for product updates or new launches.
- Ensures businesses remain proactive in dynamic markets.
PLC Marketing Strategies
Each stage of the Product Life Cycle (PLC) requires specific marketing strategies to address the product’s challenges and opportunities.
Below are the marketing strategies tailored to the five stages of the PLC:
1. Development Stage (Pre-Launch)
- Focus: Building anticipation and preparing for the launch.
- Strategies:
- Market Research: Identify target audiences and customer needs.
- Product Testing: Conduct trials to ensure product quality and functionality.
- Teaser Campaigns: Create excitement and curiosity about the upcoming product.
- Stakeholder Engagement: Inform distributors, retailers, and investors about the product.
- Example: Apple’s secretive teasers for new iPhone launches.
2. Introduction Stage
- Focus: Creating awareness and stimulating initial demand.
- Strategies:
- Promotional Campaigns: Use aggressive advertising to introduce the product.
- Pricing: Consider penetration pricing (low price to attract customers) or skimming pricing (high price for early adopters).
- Distribution Expansion: Build partnerships with retailers and distributors to ensure availability.
- Customer Education: Highlight unique features and benefits of the product.
- Example: Tesla’s extensive marketing for its electric cars emphasizing sustainability and innovation.
3. Growth Stage
- Focus: Gaining market share and maximizing sales.
- Strategies:
- Product Improvements: Introduce new features, variations, or enhancements.
- Market Penetration: Expand to new markets or customer segments.
- Pricing Adjustments: Maintain competitive pricing as competitors enter.
- Promotion: Focus on brand building and loyalty programs.
- Distribution: Increase availability through additional channels.
- Example: Samsung adding features like better cameras and displays during the growth phase of its smartphones.
4. Maturity Stage
- Focus: Retaining customers and defending market share in a saturated market.
- Strategies:
- Diversification: Offer product line extensions (e.g., new sizes, flavors, or versions).
- Loyalty Programs: Strengthen customer relationships through rewards and discounts.
- Cost Control: Reduce costs to maintain profitability amidst price wars.
- Repositioning: Target new markets or redefine the product’s value proposition.
- Advertising: Focus on differentiation and reminding customers of the product’s benefits.
- Example: Coca-Cola introducing “Coke Zero” to attract health-conscious consumers during maturity.
5. Decline Stage
- Focus: Minimizing losses and deciding whether to revive or discontinue the product.
- Strategies:
- Discounting: Use promotions to clear inventory.
- Selective Withdrawal: Retain the product in profitable markets while phasing out in others.
- Product Revitalization: Rebrand, improve, or find new uses for the product.
- Harvesting Strategy: Reduce marketing efforts and maximize remaining profits.
- Exit Strategy: Discontinue the product if it is no longer viable.
- Example: DVD players are often sold at discounted prices, while companies shift focus to streaming services.
Product Classification
Product classification refers to the grouping of products based on their characteristics, intended use, and the buying behavior of consumers.
Products are broadly classified into consumer products and industrial products.
1. Consumer Products
These are goods purchased by individuals for personal consumption.
They are further divided based on the buying behavior and frequency of use:
a. Convenience Products
Frequently purchased, low-cost items that require minimal effort in decision-making.
- Examples: Toothpaste, soap, snacks.
- Characteristics:
- Widely available.
- Purchased regularly and habitually.
- Low involvement in the buying process.
b. Shopping Products
Items for which consumers compare quality, price, and style before purchasing.
- Examples: Clothing, electronics, furniture.
- Characteristics:
- Higher price than convenience products.
- Available in fewer locations.
- Involves more time and effort in decision-making.
c. Specialty Products
Unique products with distinctive characteristics or brand loyalty.
- Examples: Luxury cars, designer clothing, gourmet foods.
- Characteristics:
- High price and exclusivity.
- Strong brand preference and loyalty.
- Consumers are willing to make special efforts to purchase.
d. Unsought Products
Products that consumers do not actively seek or are unaware of until the need arises.
- Examples: Life insurance, emergency medical services, fire extinguishers.
- Characteristics:
- Require aggressive advertising or sales efforts.
- Low purchase frequency.
2. Industrial Products
These are goods purchased by businesses for production or operational purposes. They are classified based on their usage in the production process:
a. Raw Materials
Basic materials used to produce other goods.
- Examples: Cotton, timber, iron ore.
b. Component Parts
Finished or semi-finished items used in the production of final products.
- Examples: Microchips for electronics, car tires.
c. Capital Goods
Long-term assets used in the production process.
- Examples: Machinery, buildings, tools.
d. Supplies and Services
Day-to-day operational items and services required for business operations.
- Examples: Office supplies, cleaning services, maintenance.
Importance of Product Classification
- Marketing Strategy: Helps businesses design appropriate marketing strategies based on consumer needs and buying behavior.
- Pricing Decisions: Assists in determining pricing levels for different product categories.
- Distribution: Guides the selection of suitable distribution channels.
- Promotion: Identifies the type of promotional efforts needed for each product type.
Product Line Decision
A product line is a group of related products that a company offers under the same brand.
These products share similarities in functionality, target market, or price range but cater to slightly different consumer needs.
Product line decisions involve managing the products in the line to optimize profitability, meet market demands, and strengthen the brand.
Key Product Line Decisions
1. Product Line Length
Refers to the total number of items in a product line.
- Decisions:
- Line Stretching: Adding products to the line beyond its current range.
- Downward Stretch: Adding lower-priced or basic versions of existing products to target cost-conscious consumers.
- Example: Mercedes introducing the A-Class for entry-level buyers.
- Upward Stretch: Adding higher-priced, premium versions to target luxury segments.
- Example: Toyota launching Lexus as a luxury brand.
- Two-Way Stretch: Adding products in both directions to cover a broader market.
- Example: Maruti Suzuki offering entry-level cars and premium models like Ciaz.
- Downward Stretch: Adding lower-priced or basic versions of existing products to target cost-conscious consumers.
- Line Filling: Adding more products within the existing range to meet various customer needs and prevent competitors from gaining market share.
- Example: Coca-Cola introducing Diet Coke, Coke Zero, and smaller bottle sizes.
- Line Stretching: Adding products to the line beyond its current range.
2. Product Line Depth
Refers to the variety of products or versions offered within a single product line.
- Decisions:
- Expanding Variants: Adding different sizes, flavors, or features to cater to diverse preferences.
- Example: Nestlé offering multiple flavors of Maggi noodles.
- Discontinuing Products: Removing underperforming products to optimize costs.
- Expanding Variants: Adding different sizes, flavors, or features to cater to diverse preferences.
3. Product Line Modernization
Updating or improving existing products in the line to match market trends or technological advancements.
- Example: Smartphones launching newer models with updated features like 5G compatibility.
4. Product Line Pruning
Eliminating unprofitable or outdated products from the line to focus on more profitable items.
- Example: A fashion retailer discontinuing styles that no longer sell well.
5. Product Line Consistency
Refers to how closely related the products in a line are in terms of function, target audience, or distribution channels.
- Decisions:
- Increasing consistency to build a strong brand identity.
- Reducing consistency to diversify risk and cater to different markets.
Factors Influencing Product Line Decisions
- Market Demand: Customer preferences and trends.
- Competitor Strategies: Adding or improving products to stay competitive.
- Profitability: Focusing on high-performing products.
- Company Goals: Aligning decisions with brand vision and objectives.
- Resource Availability: Managing production and distribution capacity.
Importance of Product Line Decisions
- Enhances customer satisfaction by offering diverse options.
- Strengthens market position by catering to various segments.
- Increases profitability through effective product management.
- Protects brand equity by maintaining quality and relevance.
Product Mix Decision
A product mix, also known as a product assortment, refers to the total range of products that a company offers to its customers.
Product mix decisions involve determining the breadth, depth, length, and consistency of the product assortment to optimize market coverage, customer satisfaction, and profitability.
Components of Product Mix Decisions
- Product Mix Width
Refers to the number of product lines a company offers.- Decision:
- Add new product lines to enter new markets or diversify risks.
- Consolidate or eliminate unprofitable product lines.
- Example: A company like P&G offers multiple lines, such as skincare, detergents, and personal care products.
- Decision:
- Product Mix Length
The total number of products across all product lines.- Decision:
- Add more products to existing lines to appeal to diverse customer preferences.
- Reduce the number of products to focus on top-performing ones.
- Example: A smartphone brand offering multiple models across its flagship and mid-range lines.
- Decision:
- Product Mix Depth
The number of variants offered within a specific product line. Variants can differ in size, color, flavor, or features.- Decision:
- Increase depth by introducing more variations to target different customer segments.
- Reduce depth by discontinuing less popular variants.
- Example: Colgate toothpaste offering different versions like Whitening, Herbal, and Sensitive.
- Decision:
- Product Mix Consistency
The degree of similarity between product lines in terms of use, production, and distribution.- Decision:
- Increase consistency to build brand identity and specialization.
- Diversify product lines to reduce dependence on a single market segment.
- Example: A company like Apple has high consistency, offering electronics that complement each other (iPhone, iPad, MacBook).
- Decision:
Factors Influencing Product Mix Decisions
- Market Demand: Adapting the mix to meet changing customer preferences and trends.
- Competition: Expanding or modifying the mix to counter competitors’ offerings.
- Profitability: Focusing on profitable lines and eliminating underperforming products.
- Company Resources: Managing production, distribution, and marketing resources.
- Brand Strategy: Maintaining or diversifying the brand’s image in the market.
Examples of Product Mix Decisions
- Expanding Product Mix:
- A company launches a new product line, such as a beverage brand adding snacks.
- Pruning Product Lines:
- Removing underperforming products to reduce costs and focus on profitable items.
- Adding Product Variants:
- Introducing new sizes, flavors, or features in an existing product line to appeal to more customers.
- Diversifying Product Lines:
- Entering unrelated industries to spread risks, such as a cosmetics brand introducing health supplements.
Importance of Product Mix Decisions
- Market Coverage: Cater to a broader audience with diverse needs.
- Brand Loyalty: Provide complementary products to increase customer retention.
- Competitive Advantage: Stay ahead by offering innovative or varied products.
- Profit Optimization: Focus on high-margin products and eliminate unprofitable ones.
- Risk Diversification: Spread risks across multiple product lines or categories.
Branding Decisions
Branding decisions involve creating, developing, and managing a brand to establish a strong identity in the market and build customer loyalty.
These decisions are crucial as they directly impact how a company’s products or services are perceived by consumers.
Effective branding differentiates a product from competitors, adds value to the offering, and creates a lasting impression.
Key Branding Decisions
- Brand Positioning
Defining the unique place a brand occupies in the minds of consumers.- Decisions Involved:
- Identifying the brand’s target audience.
- Highlighting unique selling propositions (USPs).
- Crafting a clear and compelling brand message.
- Example: Nike positions itself as a brand that inspires athletes and promotes an active lifestyle.
- Decisions Involved:
- Brand Name Selection
Choosing a memorable, meaningful, and easy-to-pronounce name for the brand.- Criteria for Selection:
- Reflects the product’s benefits and qualities.
- Stands out in the marketplace.
- Adaptable for different markets and languages.
- Example: Google’s name is simple, distinctive, and associated with internet search.
- Criteria for Selection:
- Brand Sponsorship
Deciding how the brand will be marketed and owned.- Types:
- Manufacturer’s Brand (National Brand): Owned by the producer (e.g., Apple, Coca-Cola).
- Private Label (Store Brand): Owned by a retailer or distributor (e.g., Kirkland by Costco).
- Licensed Brand: Using another company’s brand name (e.g., Disney licensing its characters).
- Co-Branding: Two or more brands collaborate to promote a product (e.g., Nike and Apple for the Apple Watch Nike edition).
- Types:
- Brand Development
Deciding whether to expand or refine the brand’s scope.- Strategies:
- Line Extensions: Adding variants within an existing product line (e.g., new flavors of Lay’s chips).
- Brand Extensions: Using the existing brand name to launch new products in different categories (e.g., Dove expanding from soap to hair care).
- Multibrands: Launching multiple brands in the same category (e.g., PepsiCo offering Pepsi, Mountain Dew, and 7-Up).
- New Brands: Creating an entirely new brand to target a different audience (e.g., Toyota launching Lexus).
- Strategies:
- Brand Equity Management
Building and maintaining the value of the brand in terms of consumer perception, loyalty, and market performance.- Decisions Involved:
- Consistently delivering quality and value.
- Engaging in effective marketing communication.
- Regularly monitoring consumer sentiment.
- Decisions Involved:
- Brand Repositioning
Adjusting the brand’s image to align with changing market dynamics or target audience preferences.- Example: McDonald’s repositioning itself as a healthier fast-food option with salads and other nutritious offerings.
Importance of Branding Decisions
- Differentiation: Helps distinguish products from competitors.
- Customer Loyalty: Builds trust and fosters long-term relationships with consumers.
- Higher Profit Margins: Strong brands can command premium pricing.
- Market Expansion: Facilitates easier entry into new markets or product categories.
- Brand Equity: Strengthens the value of the brand, improving both consumer perception and financial performance.
Challenges in Branding Decisions
- Intense Competition: Maintaining uniqueness in a crowded marketplace.
- Changing Consumer Preferences: Adapting the brand to evolving trends.
- Globalization: Ensuring the brand resonates with diverse cultures and markets.
- Brand Dilution Risk: Overextending the brand through excessive line or brand extensions.
Packaging & Labeling
Packaging and labeling are essential elements of product strategy.
Both play a critical role in protecting the product, attracting customers, and conveying vital information.
They serve as the first point of interaction between a product and a consumer, influencing purchasing decisions and enhancing brand recognition.
1. Packaging
Definition: Packaging refers to the design and production of a container or wrapping for a product. It involves the use of materials, colors, graphics, and text to enclose and protect the product while making it visually appealing.
Objectives/ importance of Packaging
- Protection: Prevent damage during transportation, storage, and handling.
- Example: Airtight containers for food items to maintain freshness.
- Convenience: Make the product easier to use, carry, and store.
- Example: Resealable pouches for snacks.
- Promotion: Attract customers through design and branding.
- Example: Bright, colorful packaging for children’s toys.
- Differentiation: Help the product stand out from competitors.
- Example: Coca-Cola’s iconic bottle shape.
Types of Packaging
- Primary Packaging: Directly holds the product.
- Example: A bottle for soft drinks.
- Secondary Packaging: Groups primary packages together for easier handling.
- Example: A cardboard box containing six soda bottles.
- Tertiary Packaging: Used for bulk handling and shipping.
- Example: Pallets wrapped with plastic film for transportation.
2. Labeling
Definition: Labeling refers to the information provided on the product’s packaging. It includes text, symbols, or graphics that describe the product, provide instructions, or highlight brand identity.
Objectives of Labeling
- Identification: Distinguish the product from competitors.
- Example: A brand logo on a label.
- Information: Provide details about the product’s features, usage, and contents.
- Example: Nutritional information on food items.
- Legal Compliance: Fulfill regulatory requirements.
- Example: Warning labels on cigarettes.
- Promotion: Use labels to attract attention and persuade consumers.
- Example: “Buy one, get one free” labels.
Types of Labels
- Brand Labels: Focus primarily on branding.
- Example: Nike’s logo on shoe packaging.
- Descriptive Labels: Provide detailed information about the product.
- Example: Ingredients list on packaged food.
- Grade Labels: Indicate the product’s quality or standard.
- Example: A-grade eggs.
Importance of Packaging and Labeling
- Attracts Customers: Eye-catching designs and labels help capture consumer attention.
- Builds Brand Identity: Consistent use of colors, logos, and graphics enhances brand recognition.
- Provides Information: Labels educate customers about product usage, features, and benefits.
- Ensures Safety and Compliance: Proper packaging and labeling meet legal and safety standards.
- Facilitates Convenience: Resealable, easy-to-use packaging adds value to the customer experience.
Examples in Practice
- Innovative Packaging:
- Tetra Pak for liquids ensures durability and ease of handling.
- Interactive Labeling:
- QR codes on labels allow consumers to access additional product details online.
Challenges in Packaging & Labeling
- Cost Management: Balancing quality and design with cost-effectiveness.
- Environmental Concerns: Using eco-friendly materials to meet sustainability goals.
- Regulatory Compliance: Ensuring accurate labeling to avoid legal issues.
Conclusion
Packaging and labeling are more than just functional components—they are strategic tools for marketing and brand differentiation. By combining practicality with creativity, businesses can enhance customer satisfaction, build brand loyalty, and achieve market success.
New Product Development (NPD)
New Product Development (NPD) is the process of designing, creating, and bringing a new product to market.
It involves a structured series of steps aimed at identifying market needs, generating product ideas, refining concepts, and launching a product that delivers value to customers and profitability to the company.
Steps in New Product Development
- Idea Generation
The process of brainstorming and collecting innovative ideas for new products.- Sources of Ideas:
- Internal: R&D departments, employees, and brainstorming sessions.
- External: Customer feedback, competitors, market trends, and distributors.
- Example: A cosmetics company identifies demand for eco-friendly skincare.
- Sources of Ideas:
- Idea Screening
Evaluating and filtering ideas to identify the most feasible and market-worthy ones.- Purpose: Eliminate impractical ideas early to save time and resources.
- Example: Rejecting ideas that don’t align with the company’s strengths or market demand.
- Concept Development and Testing
Turning the selected idea into a detailed product concept and testing it with a target audience.- Purpose: Determine if the concept appeals to potential customers.
- Example: Testing a prototype of a new smartphone design.
- Business Analysis
Assessing the commercial viability of the product.- Key Aspects:
- Market size and demand.
- Estimated costs and pricing strategy.
- Potential revenue and profitability.
- Example: Conducting a cost-benefit analysis for a new electric vehicle.
- Key Aspects:
- Product Development
Transforming the product concept into a tangible product through design, engineering, and prototyping.- Activities Involved:
- Developing a prototype.
- Testing functionality and quality.
- Refining the design.
- Example: Creating a working model of a wearable fitness tracker.
- Activities Involved:
- Market Testing
Launching the product in a controlled environment or test market to gauge customer reactions.- Purpose: Identify and address potential issues before full-scale launch.
- Example: Introducing a new beverage in select cities for feedback.
- Commercialization
- Definition: Full-scale production and market launch of the product.
- Activities Involved:
- Rolling out marketing campaigns.
- Ensuring distribution and availability.
- Monitoring customer feedback post-launch.
- Example: Launching a global advertising campaign for a new smartphone.
- Post-Launch Evaluation
- Definition: Analyzing the product’s performance in the market and gathering feedback for improvements.
- Example: Tracking sales data and customer reviews to identify areas of improvement.
Challenges in New Product Development
- High Costs: Developing and launching new products can be expensive.
- Market Uncertainty: Predicting customer preferences and market trends is difficult.
- Competition: Competing against established brands or innovators.
- Time Constraints: Speed-to-market is critical to gain a competitive edge.
- Technological Barriers: Implementing innovative technologies can be complex.
Importance of New Product Development
- Meeting Customer Needs: Addresses changing preferences and market gaps.
- Driving Growth: Expands the company’s product portfolio and market share.
- Competitive Advantage: Differentiates the company from competitors.
- Enhancing Profitability: Increases revenue through innovative, high-demand products.
- Adapting to Trends: Keeps the company relevant in evolving markets.
Examples of Successful NPD
- Apple iPhone: Revolutionized the smartphone market with user-friendly features and constant updates.
- Tesla’s Electric Cars: Introduced innovative, eco-friendly vehicles with advanced technologies.
- Coca-Cola Zero Sugar: Addressed health-conscious customers while retaining the brand’s essence.
Pricing Decisions: Determinants of Price
Pricing decisions involve setting the right price for a product or service to achieve business objectives, such as maximizing profits, capturing market share, or positioning the brand effectively.
The price of a product is influenced by a range of internal and external factors that determine how much customers are willing to pay and how the business can remain competitive.
Key Determinants of Price
1. Cost of Production
- The price must cover the cost of production to ensure profitability.
- Types of Costs:
- Fixed Costs: Costs that remain constant (e.g., rent, salaries).
- Variable Costs: Costs that vary with production (e.g., raw materials).
- Example: A company manufacturing a smartphone will consider the cost of components, labor, and assembly.
2. Demand for the Product
- The level of demand significantly influences pricing decisions.
- Higher Demand: Allows for higher prices.
- Lower Demand: May require discounts or promotions.
- Example: Luxury goods like Rolex watches can command high prices due to strong demand among niche customers.
3. Competition in the Market
- Prices are often influenced by competitors’ pricing strategies.
- Strategies:
- Price Matching: Offering similar prices to competitors.
- Price Undercutting: Setting a lower price to attract customers.
- Premium Pricing: Charging higher prices for better quality or exclusivity.
- Example: Airlines frequently adjust ticket prices based on competitors’ rates.
4. Target Market and Customer Perception
- The pricing decision depends on the target audience and how they perceive value.
- High-Value Perception: Allows premium pricing.
- Price Sensitivity: Requires competitive or lower pricing.
- Example: Starbucks charges a premium for coffee due to its brand image, while local cafes might use competitive pricing.
5. Objectives of the Company
- Pricing aligns with the company’s strategic goals.
- Profit Maximization: Setting a high price to generate maximum profit.
- Market Penetration: Setting a low price to attract a large customer base.
- Survival Pricing: Offering the product at a minimal price during tough market conditions.
- Example: A startup might use penetration pricing to gain market share initially.
6. Economic Conditions
- Inflation, recession, and overall economic stability affect pricing.
- Inflation: Prices are adjusted to account for rising costs.
- Recession: Lower prices may be required to encourage spending.
- Example: During a recession, companies often introduce discounts to attract customers.
7. Legal and Ethical Considerations
- Prices must comply with laws and regulations.
- Examples of Restrictions:
- Anti-price-gouging laws during crises.
- Prohibition of predatory pricing to eliminate competitors.
- Example: Governments often regulate the prices of essential medicines.
8. Product Lifecycle Stage
- Pricing strategies change depending on where the product is in its lifecycle.
- Introduction Stage: High pricing (skimming) or low pricing (penetration).
- Growth Stage: Competitive pricing to capture market share.
- Maturity Stage: Stable or discounted pricing.
- Decline Stage: Reduced prices to clear inventory.
- Example: The price of smartphones often drops as new models are introduced.
9. Distribution Channels
- Prices are influenced by the costs associated with distribution and the margins expected by intermediaries.
- Direct Sales: Lower prices due to the absence of intermediaries.
- Retail Sales: Higher prices to account for retailer margins.
- Example: A manufacturer selling directly through an e-commerce platform may charge lower prices than through traditional retail.
10. Brand Image and Positioning
- A strong brand can charge premium prices due to customer trust and loyalty.
- Premium Brands: Focus on quality and exclusivity.
- Value Brands: Focus on affordability.
- Example: Apple charges higher prices due to its brand image, while Xiaomi positions itself as a value-for-money brand.
Pricing Methods (Non-Mathematical Treatment)
Pricing methods are strategies businesses use to determine the selling price of their products or services.
These methods depend on various factors such as cost, demand, competition, and market trends.
Below are some commonly used pricing methods explained without mathematical complexity.
1. Cost-Based Pricing
- Definition: The price is determined by adding a profit margin to the cost of producing the product or service.
- Types:
- Cost-Plus Pricing: A fixed percentage is added to the cost.
- Markup Pricing: A specific markup is added to the product’s cost.
- Example: A retailer buys a product for ₹100 and adds ₹20 as profit, selling it for ₹120.
Pros:
- Simple to calculate.
- Ensures costs are covered.
Cons:
- Ignores customer demand and competition.
2. Demand-Based Pricing
- Definition: The price is set based on customer demand and perceived value.
- Key Aspect: Higher demand allows higher prices; lower demand requires discounts.
- Example: Airline tickets cost more during peak travel seasons due to higher demand.
Pros:
- Maximizes revenue during high demand.
- Focuses on customer perception.
Cons:
- Difficult to predict demand accurately.
3. Competition-Based Pricing
- Definition: Prices are set based on competitors’ pricing strategies.
- Types:
- Price Matching: Setting prices similar to competitors.
- Price Undercutting: Offering lower prices than competitors.
- Premium Pricing: Charging higher prices to position the product as superior.
- Example: An e-commerce platform offers a product for ₹5 less than a competitor to attract customers.
Pros:
- Simple to implement in competitive markets.
- Helps maintain market position.
Cons:
- May lead to price wars and reduced profits.
4. Value-Based Pricing
- Definition: Prices are based on the perceived value of the product or service to the customer, not the cost.
- Example: Luxury goods like Rolex watches are priced high because customers perceive them as valuable and exclusive.
Pros:
- Focuses on customer satisfaction.
- Allows premium pricing for quality products.
Cons:
- Requires deep understanding of customer perception.
5. Psychological Pricing
- Definition: Prices are set to influence customer perception and decision-making.
- Examples:
- Odd Pricing: Setting prices like ₹999 instead of ₹1000 to create the illusion of a better deal.
- Prestige Pricing: Charging high prices to convey quality and exclusivity.
Pros:
- Appeals to customer emotions.
- Encourages impulse buying.
Cons:
- May not work for rational customers.
6. Penetration Pricing
- Definition: Setting a low initial price to attract customers and gain market share.
- Example: A new streaming platform offers discounted subscription plans to attract users.
Pros:
- Helps establish a market presence.
- Encourages quick adoption.
Cons:
- Low profits initially.
- Difficult to increase prices later.
7. Skimming Pricing
- Definition: Setting a high initial price for a new or innovative product to maximize profits before competition increases.
- Example: A new smartphone model is priced high at launch and gradually reduced over time.
Pros:
- Recovers development costs quickly.
- Targets early adopters.
Cons:
- Attracts competition.
- May alienate price-sensitive customers.
8. Geographical Pricing
- Definition: Prices vary based on geographic location due to factors like transportation costs, local taxes, or regional demand.
- Example: A product may cost more in remote areas due to higher shipping expenses.
Pros:
- Accounts for regional cost differences.
- Maximizes profits in high-demand areas.
Cons:
- May cause customer dissatisfaction in higher-priced regions.
9. Promotional Pricing
- Definition: Temporary price reductions to boost sales or attract customers.
- Examples:
- Discounts, coupons, and sales promotions.
- Limited-time offers like “Buy One, Get One Free.”
Pros:
- Increases short-term sales.
- Attracts new customers.
Cons:
- Reduces profit margins.
- Customers may expect frequent discounts.
10. Dynamic Pricing
- Definition: Prices change based on real-time factors such as demand, time, or competition.
- Example: Ride-hailing services like Uber increase prices during peak hours (surge pricing).
Pros:
- Maximizes revenue during high demand.
- Flexible to market conditions.
Cons:
- May frustrate customers with frequent price changes.
Conclusion
The choice of pricing method depends on the company’s goals, market conditions, and customer expectations. A well-thought-out pricing strategy can drive sales, enhance brand perception, and ensure long-term profitability.
Adapting Price: Geographical Pricing, Promotional Pricing, and Differential Pricing
Adapting pricing strategies helps businesses optimize their pricing for various conditions such as location, promotions, and customer segments.
The three common types of price adaptation are Geographical Pricing, Promotional Pricing, and Differential Pricing.
Here’s a breakdown of each:
1. Geographical Pricing
Definition: Geographical pricing is a strategy where a business sets different prices for the same product or service depending on the customer’s location. This strategy takes into account factors like shipping costs, regional taxes, and local demand variations.
Types of Geographical Pricing:
- FOB Pricing (Free on Board): The buyer pays for shipping costs from the point of origin. The price is lower at the point of origin, and shipping costs are added later.
- Uniform Delivered Pricing: The company charges the same price for a product regardless of the buyer’s location, with shipping costs included in the price.
- Zone Pricing: The market is divided into geographical zones. A base price is set, and customers in different zones pay the base price plus a delivery fee based on their distance from the point of origin.
- International Pricing: Different prices are set for international customers, accounting for local production, shipping, tariffs, and local economic conditions.
Example: A company may sell a product for ₹500 in one region but ₹600 in a more distant region due to higher shipping costs.
Pros:
- Helps businesses recover additional costs due to location.
- Aligns prices with local demand and economic conditions.
Cons:
- May cause dissatisfaction among customers in higher-priced regions.
- Can be difficult to implement consistently across different regions.
2. Promotional Pricing
Definition: Promotional pricing is a temporary price reduction designed to increase short-term sales, attract customers, or stimulate demand. This type of pricing is used for special promotions, sales events, or limited-time offers.
Types of Promotional Pricing:
- Discounts and Coupons: Offering discounts or digital/physical coupons to encourage customers to buy the product.
- Flash Sales: Offering significant price reductions for a very short period.
- Bundling: Selling multiple products together at a lower price than if they were purchased individually (e.g., “Buy One, Get One Free”).
- Seasonal Promotions: Lowering prices during a particular season or event to clear inventory or attract more buyers.
Example: A retailer might offer a 20% discount on a product during the holiday season to boost sales.
Pros:
- Boosts sales in the short term.
- Attracts new customers or encourages repeat purchases.
- Effective in clearing excess inventory.
Cons:
- May lower profit margins.
- Risk of customers waiting for promotions instead of paying full price.
- Can hurt brand image if promotions are too frequent.
3. Differential Pricing (Price Discrimination)
Definition: Differential pricing, or price discrimination, is a strategy where a company charges different prices to different customers for the same product or service, based on various factors such as customer characteristics, buying behavior, or time of purchase.
Types of Differential Pricing:
- Customer Segment Pricing: Charging different prices based on customer segments, such as student discounts, senior citizen pricing, or pricing for bulk buyers.
- Time-Based Pricing: Charging different prices based on the time or season. For example, movie theaters charge lower prices during the day and higher prices at night or on weekends.
- Quantity-Based Pricing (Volume Pricing): Offering lower prices for bulk purchases, encouraging customers to buy more at a discounted price (e.g., wholesale pricing).
- Location-Based Pricing: Charging different prices based on location, as seen in geographically differentiated pricing strategies.
Example: An airline might offer lower prices for students, senior citizens, or people booking early (time-based pricing), while offering regular prices for standard customers.
Pros:
- Maximizes revenue by capturing different customer segments.
- Allows businesses to adjust pricing based on market conditions.
- Helps businesses cater to price-sensitive customers.
Cons:
- Customers may feel discriminated against or unfairly treated.
- Can be complex to manage.
- Risk of alienating certain customer groups.
Conclusion
Adapting pricing strategies helps businesses cater to different markets and customer needs effectively. Geographical pricing takes into account location-based differences, promotional pricing aims to drive short-term sales, and differential pricing helps to capture a broader market by adjusting prices based on customer segments or time. Each of these strategies provides a way to optimize revenue, increase sales, and stay competitive in diverse market conditions.
Unit 4
Promotion Mix
The Promotion Mix refers to the combination of promotional tools and strategies that a company uses to communicate its message to the target audience, build brand awareness, and stimulate demand for its products or services. The promotion mix typically includes the following elements:
Elements of Promotion Mix:
- Advertising: define
- Paid, non-personal communication.
- Examples: TV commercials, social media ads, billboards, and online banners.
- Focuses on creating awareness and reinforcing brand identity.
- Sales Promotion: ( sales promotion vs advertising )
- Short-term incentives to encourage immediate purchase.
- Examples: Discounts, coupons, buy-one-get-one offers, free samples.
- Stimulates quick sales and clears inventory.
- Public Relations (PR):
- Building a positive image and managing relationships with stakeholders.
- Examples: Press releases, charity events, sponsorships.
- Creates goodwill and strengthens brand credibility.
- Personal Selling: advantages
- Direct, face-to-face interaction between a salesperson and the customer.
- Examples: In-store sales pitches, business-to-business negotiations.
- Effective for building relationships and closing deals.
- Direct Marketing:
- Direct communication with customers to generate a response or transaction.
- Examples: Email marketing, SMS campaigns, telemarketing.
- Personalizes marketing efforts for specific customers.
- Digital/Online Marketing:
- Use of digital platforms to promote products.
- Examples: Social media marketing, search engine optimization (SEO), and influencer marketing.
- Allows precise targeting and real-time engagement.
Factors Determining Promotion Mix
Several factors influence the choice and combination of promotional tools in the promotion mix. These include:
1. Nature of the Product
- Industrial Products: Focus on personal selling and direct marketing due to technical specifications (e.g., machinery, tools).
- Consumer Products: Use advertising and sales promotions to create mass appeal (e.g., FMCG products).
2. Target Market
- Demographics: Age, gender, income, and education influence the choice of promotion.
- Geography: Urban areas may favor digital and traditional advertising, while rural areas may require local sales promotions or direct selling.
3. Stage of the Product Life Cycle (PLC)
- Introduction Stage: Focus on advertising and sales promotions to create awareness.
- Growth Stage: Emphasize advertising to reinforce the brand and personal selling to secure distribution.
- Maturity Stage: Heavy discounts and promotional offers to maintain market share.
- Decline Stage: Minimal promotions to reduce costs.
4. Budget Availability
- A large budget allows for extensive advertising and multi-channel campaigns.
- Limited budgets often rely on cost-effective strategies like social media marketing or public relations.
5. Competitive Strategy
- If competitors focus heavily on advertising, a business might need to match or differentiate its promotional efforts.
6. Marketing Objectives
- Awareness: Use advertising and PR.
- Sales: Focus on sales promotions and personal selling.
- Customer Retention: Employ loyalty programs and direct marketing.
7. Nature of the Market
- In B2B markets, personal selling and direct marketing dominate.
- In B2C markets, advertising, sales promotions, and social media marketing are key.
8. Complexity of the Product
- Complex products often require personal selling to explain features and benefits (e.g., software).
- Simple products can rely on advertising and sales promotions (e.g., snacks).
9. Technology and Media Availability
- The availability of digital platforms allows for online marketing strategies like influencer marketing and SEO.
- Traditional tools like TV and print are more suitable in areas with limited internet access.
10. Seasonality
- Products with seasonal demand, like air conditioners or holiday decor, use heavy promotions during peak seasons.
Conclusion
The promotion mix and its composition depend on a variety of factors, including the product, market, budget, competition, and customer behavior. By carefully evaluating these factors, companies can create an effective promotional strategy that aligns with their business objectives and drives customer engagement.
Promotional Tools – Basics of Advertisement, Sales Promotion, Public Relations & Publicity, and Personal Selling
Promotional tools are the techniques businesses use to communicate with their target audience and influence their purchasing decisions. Below is an explanation of the basics of key promotional tools.
1. Advertisement
Definition:
Advertising is a paid, non-personal form of promotion where businesses use various media to communicate a message about their products or services to a broad audience.
Features:
- Mass Reach: Advertising reaches a large audience at once.
- One-Way Communication: The business sends a message, but there’s no direct interaction with the audience.
- Paid Promotion: Companies pay to use media such as TV, radio, social media, and print.
Common Advertising Media:
- Traditional Media: Television, newspapers, magazines, radio, billboards.
- Digital Media: Social media ads, Google ads, YouTube promotions.
- Outdoor Media: Posters, banners, transit ads.
Purpose:
To create brand awareness, inform customers about products, and influence purchasing decisions.
2. Sales Promotion
Definition:
Sales promotion refers to short-term incentives designed to encourage customers to purchase a product or service immediately.
Features:
- Focuses on quick results and temporary demand stimulation.
- Complements other promotional tools like advertising and personal selling.
- Aims to attract new customers and retain existing ones.
Types of Sales Promotions:
- Discounts: Price reductions to stimulate sales.
- Coupons: Vouchers offering a discount on future purchases.
- Free Samples: Small quantities of a product given for free to encourage trials.
- Contests and Sweepstakes: Promotions that reward participants with prizes.
- Buy One, Get One (BOGO): Offers additional products for free or at a discount with purchase.
Purpose:
To boost short-term sales, clear inventory, or introduce new products.
3. Public Relations (PR) & Publicity
Definition:
Public relations involve building a positive image and strong relationships with the public, media, and other stakeholders. Publicity is the unpaid promotion of a brand through media coverage or word-of-mouth.
Features:
- Publicity is Earned: Unlike advertising, publicity is not paid for directly; it comes from news stories, press releases, or social media buzz.
- Credibility: PR efforts often have higher trust as they appear unbiased.
Common PR Tools:
- Press Releases: Sharing company news with media outlets.
- Event Sponsorship: Supporting events to gain visibility.
- Community Engagement: Participating in or organizing social or charitable activities.
- Crisis Management: Managing negative publicity or controversies.
Purpose:
To build goodwill, maintain a favorable public image, and handle potential issues that could harm the brand.
4. Personal Selling
Definition:
Personal selling is a direct, face-to-face interaction between a salesperson and a potential customer with the goal of influencing the customer’s purchase decision.
Features:
- Two-Way Communication: The salesperson can address customer queries and concerns in real time.
- Customized Approach: Sales pitches can be tailored to the specific needs of each customer.
- Relationship-Oriented: Builds long-term customer relationships.
Examples of Personal Selling:
- Retail sales representatives demonstrating products in stores.
- Real estate agents showcasing properties to potential buyers.
- B2B sales teams negotiating deals with business clients.
Purpose:
To provide detailed information, persuade customers, and establish trust.
Comparison of Promotional Tools
| Tool | Nature | Objective | Examples |
| Advertising | Paid, non-personal | Create awareness and reinforce brand image | TV ads, social media ads |
| Sales Promotion | Incentive-based | Stimulate short-term sales | Discounts, coupons, samples |
| Public Relations | Relationship-building | Build goodwill and handle reputation | Press releases, charity events |
| Personal Selling | Face-to-face, personal | Tailored persuasion and relationship-building | Sales presentations, demos |
Conclusion
Each promotional tool plays a unique role in marketing strategies. While advertising builds broad awareness, sales promotions drive immediate sales. PR and publicity enhance brand credibility, and personal selling fosters relationships and addresses individual customer needs. Together, they create a cohesive promotion mix for achieving marketing goals.
Unit 5
Place (Marketing Channels)
Marketing channels, also known as distribution channels, refer to the pathways through which goods or services flow from producers to customers. They play a critical role in ensuring products are available to customers when and where they need them.
1. Channel Functions
Marketing channels perform several key functions to facilitate the movement of products from producers to consumers:
a. Transactional Functions:
- Buying: Channel members purchase goods for resale to consumers or businesses.
- Selling: Actively promoting and selling products to customers.
- Risk-Taking: Bearing risks associated with holding inventory, such as damage, obsolescence, or market fluctuations.
b. Logistical Functions:
- Assorting: Bringing together a variety of products to meet customer needs.
- Storing: Maintaining inventories in warehouses for timely delivery.
- Sorting: Breaking down bulk quantities into smaller, usable sizes for consumers.
- Transporting: Physically moving products from one location to another.
c. Facilitating Functions:
- Financing: Offering credit to customers or channel members.
- Grading: Inspecting and classifying products based on quality.
- Market Information: Providing market insights, such as customer preferences and competitor activities, to producers.
2. Channel Levels
The number of intermediaries involved in the distribution process determines the channel levels:
a. Direct Channel (Zero-Level Channel):
- The producer sells directly to the consumer without intermediaries.
- Examples: Online stores, company-owned outlets.
- Advantages: Lower costs, direct customer interaction, greater control over distribution.
b. One-Level Channel:
- One intermediary, typically a retailer, is involved between the producer and the consumer.
- Examples: Producers sell to large retailers like Walmart or Target.
- Advantages: Wider reach and reduced logistical burden on producers.
c. Two-Level Channel:
- Two intermediaries, such as wholesalers and retailers, are involved.
- Flow: Producer → Wholesaler → Retailer → Consumer.
- Examples: FMCG products like packaged food and beverages.
- Advantages: Economies of scale, greater market penetration.
d. Three-Level Channel:
- Three intermediaries (agents, wholesalers, and retailers) are involved.
- Flow: Producer → Agent → Wholesaler → Retailer → Consumer.
- Examples: International or specialty goods, where agents facilitate the connection between producers and wholesalers.
- Advantages: Effective for reaching distant or fragmented markets.
Conclusion
Marketing channels play a vital role in bridging the gap between production and consumption. By performing transactional, logistical, and facilitating functions, they ensure efficient product delivery. Understanding channel levels helps businesses choose the right distribution strategy, balancing efficiency, cost, and customer reach.
Importance of Marketing Channels
Marketing channels are crucial for ensuring the effective distribution of products and services from producers to consumers. These channels bridge the gap between production and consumption, facilitating smooth transactions and delivering value to customers. Below are the key points explaining their importance:
1. Efficient Distribution of Goods
- Marketing channels streamline the movement of goods from manufacturers to consumers by handling logistics like transportation, storage, and delivery.
- They reduce the burden on producers by managing these activities, ensuring products are available when and where they are needed.
2. Market Accessibility
- Channels increase the reach of products by making them available in multiple locations, ensuring greater market coverage.
- This helps businesses tap into geographically dispersed markets, increasing sales and revenue.
3. Creation of Utility
- Place Utility: Ensures products are available where customers need them.
- Time Utility: Ensures products are available when customers need them.
- Possession Utility: Facilitates ownership transfer from seller to buyer.
4. Cost Efficiency
- By consolidating activities like warehousing, bulk buying, and distribution, intermediaries reduce the cost of logistics for producers.
- This leads to economies of scale, lowering the overall cost of delivering products to consumers.
5. Specialization and Expertise
- Intermediaries such as wholesalers and retailers specialize in distribution, logistics, and customer engagement.
- They bring expertise in managing inventory, negotiating deals, and understanding local markets, which benefits producers.
6. Improved Customer Service
- Channels ensure that customers have access to after-sales services, returns, repairs, and customer support.
- Retailers, for instance, provide product demonstrations, warranties, and assistance, improving the overall customer experience.
7. Risk Sharing
- Marketing channels absorb certain risks associated with inventory management, transportation, and product storage.
- For example, wholesalers take ownership of products, bearing the risk of unsold inventory or damage.
8. Feedback and Market Insights
- Channels act as a link between producers and customers, providing valuable feedback on customer preferences, market trends, and competitor activities.
- This helps producers refine their products and marketing strategies.
9. Promotion and Brand Building
- Retailers and distributors often participate in promotional activities such as in-store displays, advertisements, or seasonal discounts.
- These efforts help build brand awareness and boost sales.
10. Enhancing Customer Convenience
- Marketing channels make products readily available to customers through convenient locations and delivery systems.
- E-commerce platforms, for example, allow customers to shop from the comfort of their homes.
Conclusion
Marketing channels play a pivotal role in connecting producers and consumers efficiently. They reduce logistical burdens, enhance customer convenience, provide market insights, and help businesses achieve greater market penetration and customer satisfaction. By leveraging effective distribution strategies, businesses can maintain a competitive edge in the marketplace.
Types of Intermediaries: Types of Retailers and Types of Wholesalers
Intermediaries are the middle entities in the distribution process that help move goods from producers to consumers. They play a crucial role in ensuring product availability and accessibility. Below is an explanation of the types of retailers and wholesalers.
1. Types of Retailers
Retailers are intermediaries who sell goods and services directly to the end consumers. They serve as the final link in the distribution chain.
a. Store-Based Retailers:
- Department Stores:
- Large stores offering a wide range of products across multiple categories (e.g., clothing, electronics, home goods).
- Example: Macy’s, Harrods.
- Supermarkets:
- Large-scale retailers focused on groceries and household items.
- Example: Walmart, Tesco.
- Convenience Stores:
- Small stores located in residential areas offering limited products, mostly for daily needs.
- Example: 7-Eleven, local grocery shops.
- Specialty Stores:
- Focus on a specific product category or niche market.
- Example: Foot Locker (shoes), Sephora (beauty products).
- Discount Stores:
- Offer products at lower prices by focusing on high sales volumes.
- Example: Dollar General, Big Lots.
- Hypermarkets:
- Extremely large stores combining supermarkets and department stores.
- Example: Carrefour, Costco.
- Category Killers:
- Large specialty stores that dominate their category by offering a vast range of products.
- Example: IKEA (furniture), Best Buy (electronics).
- Warehouse Clubs:
- Offer bulk products at discounted prices, often requiring membership.
- Example: Costco, Sam’s Club.
b. Non-Store Retailers:
- E-commerce/Online Retailers:
- Sell products online through websites or apps.
- Example: Amazon, Flipkart.
- Direct Selling:
- Products are sold directly to consumers without a fixed retail location.
- Example: Avon, Amway.
- Telemarketing:
- Products are marketed and sold via phone calls.
- Vending Machines:
- Automated machines selling products like snacks, beverages, or small goods.
2. Types of Wholesalers
Wholesalers purchase goods in bulk from manufacturers and sell them in smaller quantities to retailers or other businesses.
a. Merchant Wholesalers:
- Independently owned firms that take title to goods and resell them.
- Full-Service Wholesalers: Provide a range of services such as storage, delivery, credit, and marketing.
- Example: Grocers’ wholesalers distributing food products.
- Limited-Service Wholesalers: Offer fewer services, such as cash-and-carry or drop shipping.
- Example: Cash-and-carry wholesalers that sell to small retailers.
b. Agents and Brokers:
- Facilitate transactions between buyers and sellers without taking ownership of goods.
- Agents: Represent buyers or sellers on a long-term basis (e.g., manufacturers’ agents).
- Brokers: Operate on a temporary basis to facilitate a specific transaction (e.g., real estate brokers).
c. Specialized Wholesalers:
- Rack Jobbers:
- Supply goods and manage inventory for retailers, often in categories like magazines or snack foods.
- Drop Shippers:
- Take orders from retailers but do not physically handle or store the products. Goods are shipped directly from the manufacturer to the retailer.
- Truck Wholesalers:
- Sell products directly from their trucks, often delivering perishable goods like fruits or dairy.
d. Manufacturers’ Sales Branches and Offices:
- Wholesaling operations owned and operated by manufacturers to sell their products directly to retailers or customers.
- Example: Coca-Cola’s distribution centers.
Conclusion
The choice of intermediaries, whether retailers or wholesalers, depends on the product type, market requirements, and distribution strategy. Retailers directly connect with end consumers, while wholesalers primarily serve as a link between producers and retailers, ensuring efficient distribution and supply chain management.
Who is a wholesaler? Function of whole and retailer in the process of marketing the goods
Wholesalers and retailers play vital roles in the distribution process by bridging the gap between producers and consumers. Their combined efforts ensure that goods move efficiently from manufacturers to end users while providing added value at each step.
Functions of Wholesalers
Wholesalers are intermediaries who buy goods in bulk from producers and sell them in smaller quantities to retailers or other businesses.
- Bulk Breaking:
- Wholesalers purchase goods in large quantities and break them into smaller units for resale to retailers.
- This reduces the burden on manufacturers and caters to the needs of small-scale retailers.
- Storage and Inventory Management:
- Wholesalers provide warehousing facilities, ensuring goods are stored safely until needed by retailers.
- They help manufacturers avoid the expense of maintaining large inventories.
- Risk Bearing:
- Wholesalers take ownership of goods and bear the risks associated with inventory, such as damage, theft, or unsold stock.
- Financing:
- They often provide credit to retailers, enabling them to purchase goods without immediate payment.
- Market Knowledge:
- Wholesalers gather valuable information about market trends, customer preferences, and demand fluctuations, which they share with manufacturers.
- Facilitation of Distribution:
- Wholesalers ensure timely delivery of goods to retailers, facilitating smooth market operations.
- Price Stabilization:
- By maintaining stock during periods of low demand and releasing it during high demand, wholesalers help stabilize prices in the market.
- Promotion Support:
- Some wholesalers assist in promoting products by offering discounts or supporting marketing campaigns initiated by manufacturers.
Functions of Retailers
Retailers are the final link in the distribution chain, selling goods directly to end consumers.
- Connecting Producers and Consumers:
- Retailers provide a platform where consumers can access products conveniently, acting as the face of the supply chain.
- Assortment of Products:
- Retailers offer a variety of goods from different manufacturers, allowing customers to choose based on their preferences.
- Customer Service:
- Retailers provide personalized services such as product demonstrations, recommendations, and assistance with returns or complaints.
- Convenience:
- They ensure goods are available in locations and quantities suitable for consumers, reducing the need for customers to purchase in bulk.
- Storage:
- Retailers maintain inventory at their stores, ensuring goods are readily available to meet consumer demand.
- Promotion and Branding:
- Retailers engage in advertising, in-store promotions, and discounts to attract customers and boost product sales.
- Feedback to Manufacturers:
- Retailers collect valuable feedback from customers about products and services, which they pass on to manufacturers for improvement.
- Price Adjustment:
- Retailers adjust prices based on market conditions, demand, and competition, ensuring affordability for consumers.
- Risk Handling:
- They bear risks associated with theft, damage, or unsold stock at the retail level.
- Creating Value for Customers:
- By offering added services like home delivery, loyalty programs, and flexible payment options, retailers enhance the overall shopping experience.
Conclusion
Wholesalers and retailers are indispensable to the marketing process. Wholesalers focus on bulk purchasing, storage, and efficient distribution to retailers, while retailers handle the final sale to consumers by providing accessibility, convenience, and customer service. Together, they ensure a smooth flow of goods from manufacturers to the end-users, creating value at every stage of the supply chain.
Marketing of Services
Marketing services differ significantly from marketing physical products due to their intangible nature and other unique characteristics. To succeed in the services sector, businesses must adopt tailored marketing strategies.
Unique Characteristics of Services
Services have distinct features that differentiate them from tangible goods. These characteristics are often summarized as the 4 I’s:
1. Intangibility:
- Services cannot be seen, touched, or physically measured before purchase.
- Example: A spa treatment or legal consultation.
2. Inseparability:
- Services are produced and consumed simultaneously, making the service provider and customer interaction essential.
- Example: A haircut or a classroom lecture.
3. Variability (Heterogeneity):
- The quality of service can vary depending on the provider, time, location, or customer.
- Example: A restaurant’s service may differ between staff or times of the day.
4. Perishability:
- Services cannot be stored for future use. Unsold service capacity is lost forever.
- Example: Empty seats on a flight or a missed hotel booking.
Marketing Strategies for Service Firms – The 7Ps
Service firms extend the traditional 4Ps of Marketing (Product, Price, Place, Promotion) by adding three additional elements specific to services: People, Process, and Physical Evidence.
1. Product:
- Focus on the quality, features, and design of the service.
- Ensure the service meets customer needs and expectations.
- Example: A bank offering customized financial advice.
2. Price:
- Pricing strategies depend on demand, competition, and perceived value.
- Include dynamic pricing, seasonal pricing, and bundling.
- Example: Surge pricing for rideshare services during peak hours.
3. Place:
- Ensure service accessibility through physical locations or digital platforms.
- Use online apps, service centers, or mobile services.
- Example: Food delivery apps providing services via mobile.
4. Promotion:
- Highlight the benefits and quality of the service through advertising, social media, and word-of-mouth.
- Build trust with testimonials and case studies.
- Example: Hospitals promoting success stories or satisfied patient feedback.
5. People:
- Service quality depends on the interaction between customers and employees.
- Train employees to deliver excellent customer service and maintain professionalism.
- Example: Airlines ensuring staff are well-trained in customer care.
6. Process:
- Focus on delivering services efficiently and consistently.
- Standardize procedures to ensure quality while being adaptable to customer needs.
- Example: Fast food chains optimizing their order and delivery process.
7. Physical Evidence:
- Since services are intangible, tangible elements like ambiance, uniforms, or certificates help customers evaluate the service.
- Example: A well-maintained office for a consulting firm or a clean, modern interior for a restaurant.
Conclusion
Marketing services require strategies that address their intangible, variable, inseparable, and perishable nature. By focusing on the 7Ps framework, service firms can deliver superior customer experiences, build trust, and remain competitive in the market.
Define
Consumer Durables
Direct Marketing
Product Branding
Pricing
Franchising
Elements of marketing mix
Diff goods & services
Diff Marketing and Selling
Diff Brand & Trademark
Diff Advertising & sales promotion
Scope of Mark


Thanks a lot for these notes. It helps a lot during the exams.